【鸿蒙开发 day14】
本章主要学习了ArkTs中的条件分支语句和循环的一些语法,让我们使用分支去实现控制渲染,用循环去遍历数组.
·
鸿蒙开发核心-基础
一.分支语句
1.语句的概念
● 表达式: 可以被求值的代码,并将其计算出一个结果
● 语句: 一段可以执行的代码,是一个行为,例如分 支语句和循环语句
2.if分支
if 语句用于需要根据逻辑条件执行不同语句的场景。当逻辑条件为真时,执行对应的一组语句。
3.单分支语句
- 语法: if(条件){条件成立执行的代码}
- 条件: 转为布尔值,为true为条件成立 为false条件不成立
- 小括号内的结果若不是布尔类型时,会发生类型转换为布尔值
- 大括号如果只有一条语句可以省略大括号
let grade:number = 400
if (grade>=400){
console.log('','65')
}
if (grade>222)
//只有一条语句,大括号可以省略
console.log('','学习鸿蒙知识')
4.双分支
- 语法:if(条件){成立执行的代码} else{条件不成立执行的代码}
//成绩
let score:number = 700
if (score >=750){
console.log('','满分')
}else {
console.log('高手',)
}
5.多分支语句
- if多分支语句
- 语法:
- if(条件1){代码1}
- else if(条件2){代码2}
- …
- else{以上条件全都不成立执行的代码}
let score:number = 60
if (score>90){
console.log(`成绩很优秀`)
}else if (score>=70){
console.log('成绩良好')
}else if(score>=60){
console.log(`成绩合格`)
}else{
console.log('成绩不合格')
}
6.三元表达式
- 三元表达式
- 语法: 条件? 条件成立时候执行的代码:条件不成立执行的代码
例子:两个数找最大值
let num1: number = 120
let num2: number = 100
let res:number = num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2
console.log('最大值是: ',res)
二.购物车案例
主要是实现加减单子的数量,要求数量大于0才可以点击减号,进行减少数量,如果小于0
点击减号提示购物车为空了,不能再减了
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State count:number = 1
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Text('-')
.width(20)
.height(20)
.border({width: 1, color: '#999', radius: {topLeft: 3, bottomLeft:3}})
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.onClick(()=>{
if (this.count>0) {
this.count--
}else {
AlertDialog.show({
message:'购物车已经空了不能再减了'
})
}
})
Text(this.count.toString())
.height(20)
.padding({left: 10, right: 10})
.border({width: {top: 1, bottom: 1}, color: '#999'})
.fontSize(14)
Text('+')
.width(20)
.height(20)
.border({width: 1, color: '#999', radius: {topRight: 3, bottomRight: 3}})
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.onClick(()=>{
this.count++
})
}
}
.padding(20)
}
}
三.switch分支
switch (表达式) {
case 值1:
与值1匹配执行的语句
break
case 值2:
与值2匹配执行的语句
break
default:
以上都未成功匹配执行的代码
}
注意: 如果没有break语句,则继续执行switch中的下一条case语句
let age: number = 18
switch (age) {
case 18:
console.log('你已经成年了')
break
case 30:
console.log('30碎了')
break
case 50:
console.log('50岁了')
break
case 90:
console.log('九十岁了')
break
default:
console.log('年龄输入有误')
}
四.单击切换案例
这个案例有两种写法,第一种需要申明三个状态变量
而第二种只需要声明一个状态变量,结合三元表达式
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State colors: Color = Color.Blue
@State text: string = '+ 关注'
@State flag: boolean = false
build() {
Column() {
Button(`${this.flag ? '已关注' : '+ 关注'}`)
.onClick((event: ClickEvent) => {
//方法一:
// if(!this.flag){
// this.text = '已关注'
// this.colors=Color.Orange
// this.flag = !this.flag
// }else{
// this.text = '+ 关注'
// this.colors=Color.Blue
// this.flag = !this.flag
// }
//三元运算符实现
this.flag = !this.flag
})
.width(150)
.height(80)
.fontSize(20)
.fontColor('#fff')
.backgroundColor(`${this.flag ? Color.Orange : Color.Blue}`)
.fontWeight(600)
}.width('100%')
}
}
运行结果:
五.条件渲染
- ArkTS提供了渲染控制的能力。条件渲染可根据应用的不同状态,使用if、else和else if渲染对应状态下的UI内容。
- if、else if后跟随的条件语句可以使用状态变量,状态变量值变化时,条件渲染语句会进行更新。
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
//定义状态变量
@State count:number = 1
build() {
Column({space:20}){
//条件渲染
if (this.count == 1){
Text('1')
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
}else if (this.count == 2){
Text('2')
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
}else if (this.count == 3){
Text('3')
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
}else{
Text(this.count.toString())
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
Button('点击按钮切换').onClick((event: ClickEvent) => {
this.count++
})
}.width('100%')
}
}
运行结果: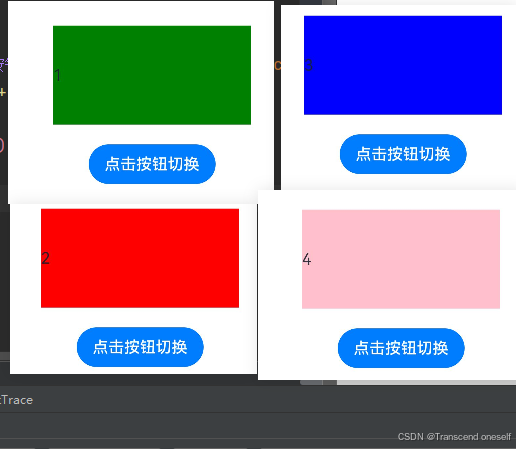
六.条件渲染-京东购物案例
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State count:number = 0
build() {
Column() {
Column() {
// 底部菜单
Row({space: 10}) {
// 左侧菜单
Row() {
Column({space: 5}) {
Image($r('app.media.ic_dianpu'))
.width(20)
Text('店铺')
.fontSize(10)
.fontColor('#262626')
}
Column({space: 5}) {
Image($r('app.media.ic_kefu'))
.width(20)
.fillColor('#666')
Text('客服')
.fontSize(10)
.fontColor('#262626')
}
Column({space: 5}) {
Image($r('app.media.ic_cart2'))
.width(20)
.fillColor('#666')
Text('购物车')
.fontSize(10)
.fontColor('#262626')
}
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
// 右侧按钮 -- 可以购买
if (this.count>0){
Row({space: 5}) {
Button('加入购物车')
.width(105)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#ffcc00')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(600)
Button('立即购买')
.width(105)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#f92c1b')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(600)
}
}else{
//右侧按钮 -- 不能购买
Row() {
Button('查看类似商品')
.width(170)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#ffcc00')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(600)
}
}
}
.width('100%')
.height(60)
.backgroundColor('#f7f7f7')
.padding({left: 20, right: 10})
// 消息提示:库存 <= 0 显示,否则隐藏
if (this.count<=0){
Row() {
// 左侧
Row({ space: 5 }){
Image($r('app.media.ic_lingdang'))
.width(12)
.fillColor('#de6a1c')
Text('该商品暂时没有库存,看看相似商品吧')
.fontSize(10)
.fontColor('#de6a1c')
}
// 右侧
Image($r('app.media.ic_shangjiantou'))
.width(15)
.padding(3)
.fillColor('#d0662c')
.backgroundColor('rgba(0,0,0,0.1)')
.borderRadius(8)
}
.width('100%')
.height(36)
.backgroundColor('#fbf9da')
.position({x: 0, y: '-36'})
.padding({left: 20, right: 20})
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
}
}
.position({x:0,y:'100%'})
.translate({y: '-100%'})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding({bottom:20})
.backgroundColor('#f2f2f2')
}
}
运行结果: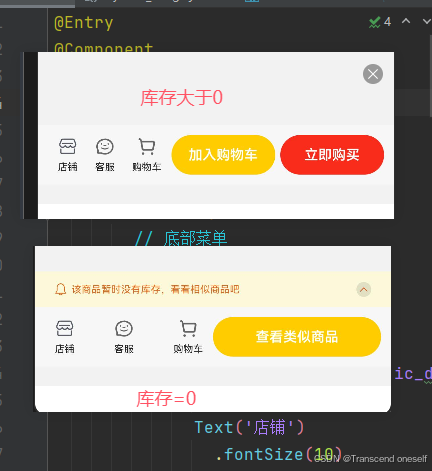
七.while循环
- while循环三要素
- 1.初始值
- 2.循环条件
- 3.变化值(使得初始值逼近循环条件结束)
- 语法while(条件){代码块}
循环打印1~100
let num:number =1
while (num<=100){
console.log(`${num}\t`)
num++
}
打印1~100的和
let num: number = 1
let sum: number = 0
while (num <= 100) {
//计算1~100的和
sum += num
num++
}
console.log('1~100的和: ', sum)
八.for循环
- for循环
- 语法: for(初始值;条件;变化量){满足条件重复执行的代码}
循环输出1~100
for (let i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
console.log('', i)
}
计算1~100的和
let sum: number = 0
for (let j = 1; j <= 100; j++) {
sum += j
}
console.log('sum = ',sum)
- 遍历数组的每一项
let names:String[] = ['至尊宝','天山','蚩尤','麒麟']
//遍历数组的每一项
for (let i= 0;i<names.length;i++){
console.log('',names[i])
}
运行结果;
九.break和continue
- break :跳出整个循环
- continue : 跳过本次循环,进行下一次循环
for (let i = 1;i<=5;i++){
if (i==3)
break;
console.log('break',i)
}
for (let j = 1;j<5;j++){
if (j==3)
continue
console.log('continue',j)
}
运行结果: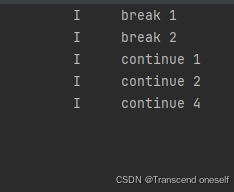
十.for … of的使用
- 遍历数组
- 语法 for(let 变量名 of 数组名){}
let names:string[] = ['至尊宝','紫霞','蚩尤','剑圣','高斯']
for (let name of names){
console.log('',name)
}
运行结果: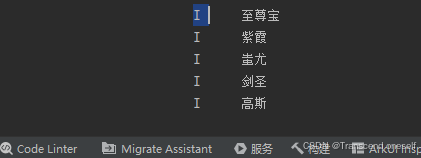
十一.总结
本章主要学习了ArkTs中的条件分支语句和循环的一些语法,让我们使用分支去实现控制渲染,用循环去遍历数组.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)