移植案例与原理 - startup子系统之bootstrap_lite部件 (2)
在文件base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\bootstrap_service.h中定义了2个宏函数INIT_APP_CALL和INIT_TEST_CALL,分别用来调用代码段&__zinitcall_app_XXX_start、&__zinitcall_app_XXX_end和&__zinitcall_test_start、&__zinitcal
往期知识点记录:
- 鸿蒙(HarmonyOS)应用层开发(北向)知识点汇总
- startup子系统之syspara_lite系统属性部件 (1)
- startup子系统之syspara_lite系统属性部件 (2)
- startup子系统之bootstrap_lite服务启动引导部件(1)
- startup子系统之bootstrap_lite部件 (2)
- utils子系统之file文件操作部件
- utils子系统之KV存储部件 (1)
- utils子系统之KV存储部件 (2)
- utils子系统之KV存储部件 (3)
- build lite配置目录全梳理
- build lite编译构建过程
- XTS子系统之应用兼容性测试用例开发
- XTS子系统之应用兼容性测试套件(1)
- XTS子系统之应用兼容性测试套件(2)
- HPM包描述文件bundle.json
- build lite源码分析 之 hb命令__main__.py
- 持续更新中……
2.3 OHOS_SystemInit函数
函数OHOS_SystemInit()定义在文件base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\system_init.c,代码如下。调用宏函数MODULE_INIT、SYS_INIT和函数SAMGR_Bootstrap()进行初始化启动。
void OHOS_SystemInit(void)
{
MODULE_INIT(bsp);
MODULE_INIT(device);
MODULE_INIT(core);
SYS_INIT(service);
SYS_INIT(feature);
MODULE_INIT(run);
SAMGR_Bootstrap();
}
我们详细分析下宏函数MODULE_INIT和SYS_INIT的源代码,这2个宏函数在文件base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\core_main.h中定义,代码如下。这些宏函数的参数大都为name和step,name取值为bsp、device、core、service、feature、run,step取值为0。从⑺和⑻处可以看出,分别调用SYS_CALL、MODULE_CALL两个宏,第二个参数设置为0。⑸处定义的MODULE_BEGIN函数,用于返回链接脚本中定义的代码段的开始地址,当传入参数为bsp时,返回&__zinitcall_bsp_start,MODULE_BEGIN函数被展开为如下片段:
{ extern InitCall __zinitcall_sys_start; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_bsp_start; \
(initCall); \
}
⑹处定义的MODULE_END函数,用于返回链接脚本中定义的代码段的结束地址,当传入参数为bsp时,返回&__zinitcall_bsp_end,MODULE_END函数被展开为如下片段:
{ extern InitCall __zinitcall_bsp_end; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_bsp_end; \
(initCall); \
}
⑶和⑷处定义的SYS_BEGIN、SYS_END代码类似,分于返回链接脚本中定义的标记系统服务或特性的代码段的开始、结束地址,即&__zinitcall_sys_service_start、&__zinitcall_sys_service_end、&__zinitcall_sys_feature_start、&__zinitcall_sys_feature_end。⑴处定义的SYS_CALL函数,分别获取链接脚本中zInit代码段的开始initcall和结束地址initend,这些地址存放的是初始化函数的地址,语句 (*initcall)()会循环调用执行这些初始化函数。⑵处MODULE_CALL宏类似。
⑴ #define SYS_CALL(name, step) \
do { \
InitCall *initcall = (InitCall *)(SYS_BEGIN(name, step)); \
InitCall *initend = (InitCall *)(SYS_END(name, step)); \
for (; initcall < initend; initcall++) { \
(*initcall)(); \
} \
} while (0)
⑵ #define MODULE_CALL(name, step) \
do { \
InitCall *initcall = (InitCall *)(MODULE_BEGIN(name, step)); \
InitCall *initend = (InitCall *)(MODULE_END(name, step)); \
for (; initcall < initend; initcall++) { \
(*initcall)(); \
} \
} while (0)
......
⑶ #define SYS_BEGIN(name, step) \
({ extern InitCall __zinitcall_sys_##name##_start; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_sys_##name##_start; \
(initCall); \
})
⑷ #define SYS_END(name, step) \
({ extern InitCall __zinitcall_sys_##name##_end; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_sys_##name##_end; \
(initCall); \
})
⑸ #define MODULE_BEGIN(name, step) \
({ extern InitCall __zinitcall_##name##_start; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_##name##_start; \
(initCall); \
})
⑹ #define MODULE_END(name, step) \
({ extern InitCall __zinitcall_##name##_end; \
InitCall *initCall = &__zinitcall_##name##_end; \
(initCall); \
})
⑺ #define SYS_INIT(name) \
do { \
SYS_CALL(name, 0); \
} while (0)
⑻ #define MODULE_INIT(name) \
do { \
MODULE_CALL(name, 0); \
} while (0)
3、 bootstrap_lite服务启动引导部件实现原理之bootstrap_service
在文件base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\bootstrap_service.h中定义了2个宏函数INIT_APP_CALL和INIT_TEST_CALL,分别用来调用代码段&__zinitcall_app_XXX_start、&__zinitcall_app_XXX_end和&__zinitcall_test_start、&__zinitcall_test_end之间的初始化启动函数。bootstrap_service.h文件中的宏和base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\core_main.h文件中的宏类似,不再一一分析。
3.1 结构体struct Bootstrap
在文件base\startup\bootstrap_lite\services\source\bootstrap_service.c中定义了结构体struct Bootstrap,如下代码⑵处。其中结构体中的INHERIT_SERVICE定义在文件foundation/distributedschedule/samgr_lite/interfaces/kits/samgr/service.h,见代码片段⑴处。
⑴ #define INHERIT_SERVICE \
const char *(*GetName)(Service * service); \
BOOL (*Initialize)(Service * service, Identity identity); \
BOOL (*MessageHandle)(Service * service, Request * request); \
TaskConfig (*GetTaskConfig)(Service * service)
......
⑵ typedef struct Bootstrap {
INHERIT_SERVICE;
Identity identity;
uint8 flag;
} Bootstrap;
结构体Identity定义在文件foundation\distributedschedule\samgr_lite\interfaces\kits\samgr\message.h中,用于标识一个服务或特性。
/**
* @brief Identifies a service and feature.
*
* You can use this structure to identity a {@link IUnknown} feature to which messages will be
* sent through the asynchronous function of {@link IUnknown}. \n
*
*/
struct Identity {
/** Service ID */
int16 serviceId;
/** Feature ID */
int16 featureId;
/** Message queue ID */
MQueueId queueId;
};
3.2 Init(void)函数
讲解移植适配示例时,我们已经知道,bootstrap_lite部件会编译//base/startup/bootstrap_lite/services/source/bootstrap_service.c,该文件通过函数宏SYS_SERVICE_INIT将Init()函数符号灌段到__zinitcall_sys_service_start和__zinitcall_sys_service_end代码段中,代码片段如下。下文再详细分析GetName、Initialize、MessageHandle和GetTaskConfig函数。
static const char *GetName(Service *service);
static BOOL Initialize(Service *service, Identity identity);
static TaskConfig GetTaskConfig(Service *service);
static BOOL MessageHandle(Service *service, Request *request);
static void Init(void)
{
static Bootstrap bootstrap;
bootstrap.GetName = GetName;
bootstrap.Initialize = Initialize;
bootstrap.MessageHandle = MessageHandle;
bootstrap.GetTaskConfig = GetTaskConfig;
bootstrap.flag = FALSE;
SAMGR_GetInstance()->RegisterService((Service *)&bootstrap);
}
SYS_SERVICE_INIT(Init);
3.3 GetName和Initialize函数
GetName函数代码如下,其中BOOTSTRAP_SERVICE定义在文件foundation\distributedschedule\samgr_lite\interfaces\kits\samgr\samgr_lite.h中,取值为"Bootstrap",表示启动引导服务。
static const char *GetName(Service *service)
{
(void)service;
return BOOTSTRAP_SERVICE;
}
Initialize函数定义如下,用于设置启动引导服务的标识信息。
static BOOL Initialize(Service *service, Identity identity)
{
Bootstrap *bootstrap = (Bootstrap *)service;
bootstrap->identity = identity;
return TRUE;
}
3.4 MessageHandle函数和GetTaskConfig函数
MessageHandle函数和GetTaskConfig函数代码如下,MessageHandle函数用于处理各种请求,请求消息编号定义request->msgId定义在文件foundation\distributedschedule\samgr_lite\interfaces\kits\samgr\samgr_lite.h中的枚举enum BootMessage,如下⑴处所示。在MessageHandle函数中,当请求的消息编号为BOOT_SYS_COMPLETED系统服务初始化完成时,检查应用服务是否加载。当应用没有加载时,执行INIT_APP_CALL宏函数调用zInit代码段上的应用服务和应用特性初始化函数。然后执行⑶,调用函数SAMGR_SendResponseByIdentity进行响应。GetTaskConfig函数用于获取任务配置。
⑴ typedef enum BootMessage {
/** Message indicating that the core system service is initialized */
/** 标识核心系统服务初始化完成 */
BOOT_SYS_COMPLETED,
/** Message indicating that the system and application-layer services are initialized */
/** 标识应用层服务初始化完成 */
BOOT_APP_COMPLETED,
/** Message indicating service registration during running */
/** 标识运行时的服务注册 */
BOOT_REG_SERVICE,
/** Maximum number of message IDs */
/** 标识消息最大值,butt是烟蒂;屁股;枪托的意思,表示尾部吧 */
BOOTSTRAP_BUTT
} BootMessage;
......
static BOOL MessageHandle(Service *service, Request *request)
{
Bootstrap *bootstrap = (Bootstrap *)service;
switch (request->msgId) {
case BOOT_SYS_COMPLETED:
⑵ if ((bootstrap->flag & LOAD_FLAG) != LOAD_FLAG) {
INIT_APP_CALL(service);
INIT_APP_CALL(feature);
bootstrap->flag |= LOAD_FLAG;
}
⑶ (void)SAMGR_SendResponseByIdentity(&bootstrap->identity, request, NULL);
break;
case BOOT_APP_COMPLETED:
(void)SAMGR_SendResponseByIdentity(&bootstrap->identity, request, NULL);
break;
case BOOT_REG_SERVICE:
(void)SAMGR_SendResponseByIdentity(&bootstrap->identity, request, NULL);
break;
default:
break;
}
return TRUE;
}
static TaskConfig GetTaskConfig(Service *service)
{
(void)service;
// The bootstrap service uses a stack of 2 KB (0x800) in size and a queue of 20 elements.
// You can adjust it according to the actual situation.
TaskConfig config = {LEVEL_HIGH, PRI_NORMAL, 0x800, 20, SHARED_TASK};
return config;
}
小结
本文介绍了startup子系统之bootstrap_lite服务启动引导部件的移植适配案例及原理。
经常有很多小伙伴抱怨说:不知道学习鸿蒙开发哪些技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?
为了能够帮助到大家能够有规划的学习,这里特别整理了一套纯血版鸿蒙(HarmonyOS Next)全栈开发技术的学习路线,包含了鸿蒙开发必掌握的核心知识要点,内容有(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、WebGL、元服务、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、OpenHarmony驱动开发、系统定制移植等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)技术知识点。

《鸿蒙 (Harmony OS)开发学习手册》(共计892页):https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
如何快速入门?
1.基本概念
2.构建第一个ArkTS应用
3.……
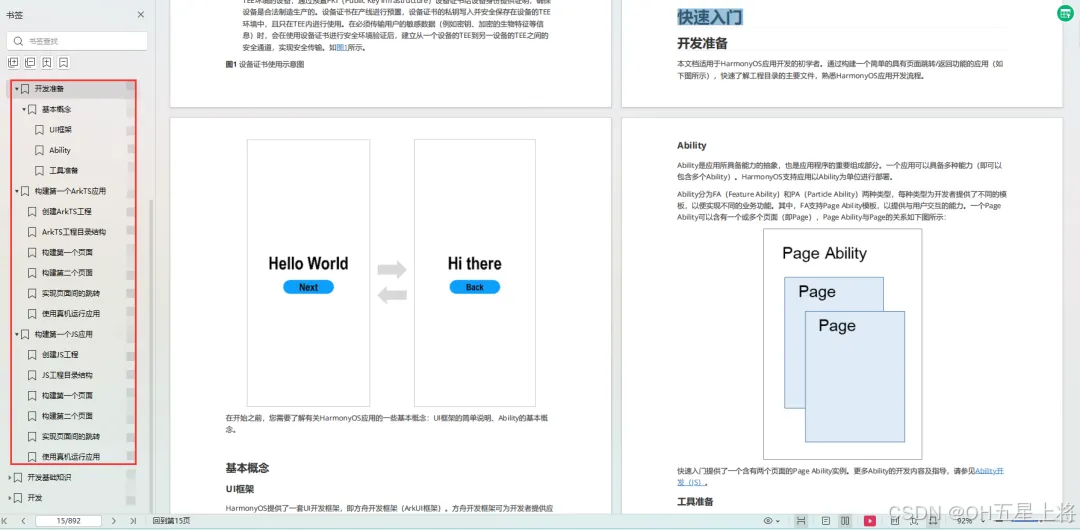
开发基础知识:
1.应用基础知识
2.配置文件
3.应用数据管理
4.应用安全管理
5.应用隐私保护
6.三方应用调用管控机制
7.资源分类与访问
8.学习ArkTS语言
9.……

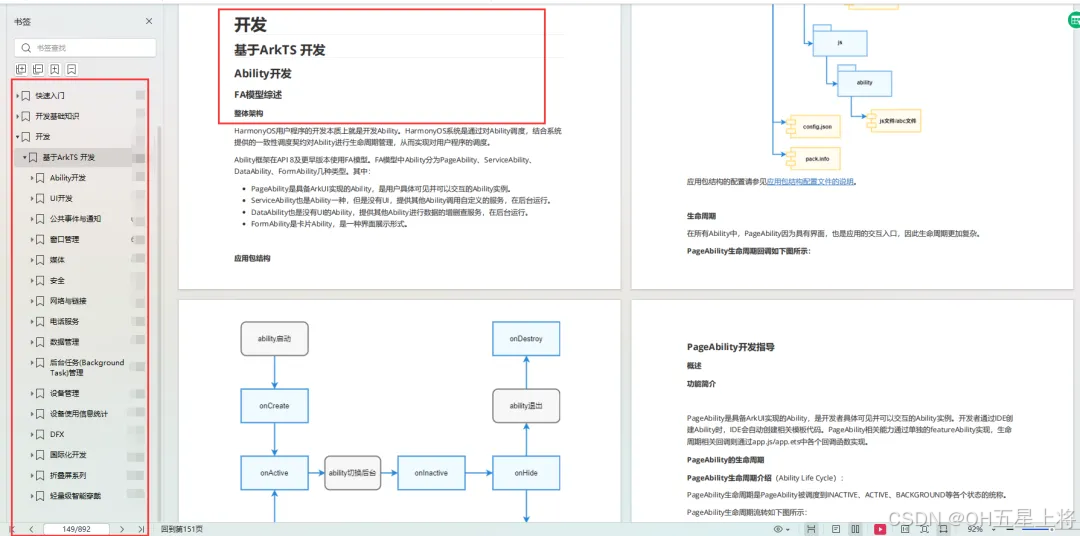
基于ArkTS 开发
1.Ability开发
2.UI开发
3.公共事件与通知
4.窗口管理
5.媒体
6.安全
7.网络与链接
8.电话服务
9.数据管理
10.后台任务(Background Task)管理
11.设备管理
12.设备使用信息统计
13.DFX
14.国际化开发
15.折叠屏系列
16.……
鸿蒙开发面试真题(含参考答案):https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
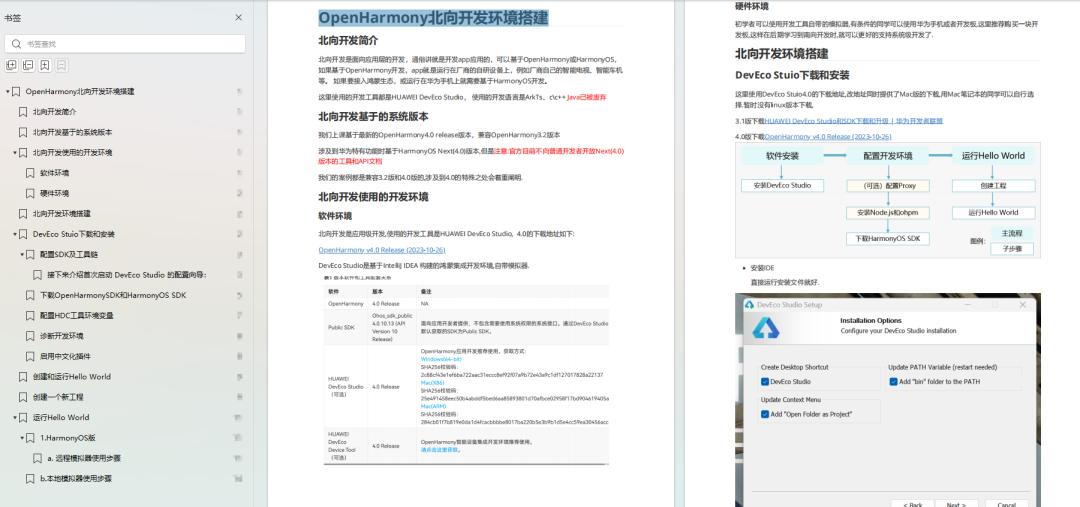
OpenHarmony 开发环境搭建
《OpenHarmony源码解析》:https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
- 搭建开发环境
- Windows 开发环境的搭建
- Ubuntu 开发环境搭建
- Linux 与 Windows 之间的文件共享
- ……
- 系统架构分析
- 构建子系统
- 启动流程
- 子系统
- 分布式任务调度子系统
- 分布式通信子系统
- 驱动子系统
- ……

OpenHarmony 设备开发学习手册:https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview


更多推荐
 已为社区贡献43条内容
已为社区贡献43条内容







所有评论(0)