时间序列分类算法ST及其实现代码
时间序列分类(TSC)问题对分类算法提出了一个特殊的挑战:如何度量序列间的相似性。shapelet是一个时间序列子序列,它允许基于形状的局部、相位无关相似性进行时间序列分类。(Shapelets是时间序列的辨别性子序列,可以最好地预测目标变量)。基于shapelet的分类使用shapelet和序列之间的相似性作为辨别性特征。shapelet方法的一个好处是shapelet是可理解的,并且可以提供对
基于shapelets转换的时间序列分类
介绍
时间序列分类在金融[Zheng2008A](Supervised classificationofshare price trends)、医学[Costa2009A](Constrained mixture estimation for analysis and robust classification of clinical time series)等学科中发挥着重要的作用。尽管可以将每个时间点的值作为一个特征,并使用一个规则的分类器(如最近邻欧氏距离)进行时间序列分类,但该分类器可能对时间轴的失真敏感,并且会导致精度性能不理想。具有动态时间扭曲(nndtw)的最近邻对时间轴的失真具有鲁棒性,并且证明了其异常难以被打败[Xi2006A](Fast time series classification using numerosity reduction)。然而,nndtw对于区分时间序列和不同类别的时间特征提供了有限的见解。
时间序列分类方法可分为基于实例的和基于特征的。基于实例的分类器根据其与测试的相似性来对其类标进行预测。在基于实例的分类器中,基于欧几里得距离或动态时间规整的最近邻分类器已经被广泛且成功的使用(Making time-series classificationmore accurate using learned constraints)(Early prediction ontime series:anearest neighbor approach)(Dynamic time warping constraint learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification)。通常NNDTW分类器优于NNEucilidean分类器(DTW[Sakoe1978A](Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition)对时间轴失真有鲁棒性),被认为是解决时间序列问题较好的方法[Ratanamahatana2005A](Three myths about dynamic time warping data mining])。基于实例的分类器可能是正确的,但它们提供的对于那些对分类有用的时间特征的洞察力不够。
基于特征的分类器利用时间特征构建分类器,比基于实例的分类器有更多潜在的可解释性。基于特征的分类器通常包含两个步骤:定义时间特征然后根据定义的时间特征构建分类器。
时间序列研究引起了数据挖掘界的极大兴趣,因为时间序列数据广泛存在于各个现实领域中。时间序列数据通常表现出较小的子序列而非整条序列结构的类间差异[Ye2009A]。在时间序列分类问题中,类标签应用于未标记的有序数据集。数据不需要临时组织;任何的有逻辑顺序的数据都是可用的(比如,图形就可以用时间序列来表示,如图1-1所示)。对于传统的分类问题而言,属性的顺序是不重要的,并且变量之间的相互关系独立于它们的相对位置。而对于时间序列数据而言,变量间的顺序对于寻找最佳的辨别性特征有着至关重要的作用。时间序列分类研究集中在基于原始数据或压缩或平滑数据的最近邻分类器的可替代距离度量上面(综合介绍参考[Deng2008A])。实验表明,与弹性度量相结合的1-NN分类算法,比如动态时间规整(DTW),是对于较小数据集的最好分类方法;然而,随着时间序列数量的增多,弹性度量的精度趋于与欧氏距离的精度一致[Deng2008A]。这一观点在当前的研究中得到了广泛认可。比如,Batista等人指出“有大量的分类算法可以应用于时间序列;然而,所有现有的经验证据表明,简单的最近邻分类是很难被打败的”[Batista2011A]。最近,出现了几种替代性距离度量方法,比如加权动态时间规整[Jeong2010A],建立在变量间隔上的支持向量机[Rodriguez2005A],基于汇总统计的树集成[Deng2011A],和替代距离度量的融合[Buza2011A]。
这些方法集中在以下问题上:每个类的序列都是对时间维度中潜在公共曲线的观测值。在这个基础形状周围的变化是由观测中的噪声和索引中的噪声引起的,这些噪声可能会引起轻微的相位偏移。这种相似性的一个典型例子是圆柱形钟形漏斗人工数据集,它的基本形状周围和形状转换的索引中都存在噪声。直观地说,时域NN分类器是解决这类问题的理想工具,因为DTW可以用来减轻索引中的噪声。还有一组问题涉及到形状相似性定义类成员的情况。一个类中的序列可以用与相位无关的常见子形状来区分;定义形状可以从系列中的任何点开始。如果定义类成员的底层相位无关形状是全局的,也就是说,形状大约是序列的长度,那么可以使用基于频域变换的技术来构造分类器[Janacek2005A]。然而,如果辨别性形状是局部的,即比整条时间序列要短很多,因此,不太可能用一般的方法检测类与类之间的差异。[Ye2009A]中提出了shapelets来解决此类问题。
shapelet是一个时间序列子序列,它可以作为时间序列的基元,基于形状的局部、相位无关相似性。基于shapelet的分类包括测量shapelet和每个系列之间的相似性,然后将这种相似性作为分类的一个辨别性特征。原始的基于shapelet的分类器将shapelet发现算法嵌入到决策树中,并使用信息增益来评估候选对象的质量。通过枚举搜索在树的每个节点上找到shapelet。shapelets 已经被应用到早期分类[Xing2012A],手势识别[Hartmann2010A],步态识别[Sivakumar2012A]和聚类中[Zakaria2012A]。
对shapelets的详尽搜索非常耗时。因此,对shapelets的主要研究都集中在加速搜索的技术上[He2012A][Mueen2011A][ Rakthanmanon2013A][Ye2009A][Ye2011A]。这些研究都着眼于改善或者说加速shapelets的搜索,但是没有考虑如何最好的用shapelets解决分类问题。决策树是非常有用的健壮分类器,但是在许多问题领域都被其他分类器超越,比如支持向量机,贝叶斯网络和随机森林。
我们提出了一种单扫描算法,在一组n个时间序列中找到最佳的k个shapelets。我们用该算法生成一个转换数据集,其中k个特征分别对应每一个shapelets和时间序列的数据集。也就是说新数据集的第j条记录的第i个属性值代表的是原数据集中第j条时间序列和第i个shapelets的距离。该方法的主要优点在于,我们可以将任何分类器和转换数据集进行结合来进行分类,并且我们不必在每个节点上按顺序搜索shapelet。对shapelet转换进行线程处理是一个令人尴尬的并行问题。
由转换生成的许多shapelets彼此类似。在准确性方面,如果使用的分类器能够处理相关属性,这不是一个问题;但是,它确实降低了转换数据集的可解释性。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了一个后转换聚类过程,将相似的形状分组(跟删除相似比哪个更好?)。我们证明了这种降维可以使我们轻松地将形状映射回问题域,而不会大大降低分类器的精度。
我们也解决了如何评估shaplets的质量。测量每个候选shapelet和每个系列之间的相似性,并使用具有相关类成员关系的距离序列评估shapelet质量。构造递归决策树的一个含义是,需要根据距离序列在每个节点上找到一个分割点。这一要求使得自然地使用信息增益作为shapelet质量度量。但是,计算连续属性的信息增益需要计算所有拆分点,并且只计算二进制拆分。这会带来时间开销,意味着对于多类问题,信息增益可能无法完全捕获shapelet的质量。相反,在构造shapelet转换时不需要拆分数据。因此,我们可以将质量度量建立在对类群之间距离分布差异进行假设检验的基础上。这使我们能够全面评估多类问题,并提供一些速度改进。我们在均值差异方差检验分析的基础上进行了测度试验,以及非参数Kruskal-Wallis和情绪中位数检验中位数差异。
我们在29个数据集上进行了实验,其中17个来自UCR数据集,另外12个数据集是我们自己提供的。该研究是[Lines2012A][Lines2012B]工作的延伸。代码和数据集可以从[Bagnall2012A]获得。我们的贡献可以概括如下:
(1)我们描述了一个shapelet发现算法,在单次传递中找到最好的k 个shapelet,并在基准时间序列数据集和新数据上通过大量实验对其进行评估。
(2)我们评估了用于我们的算法的三个可选质量度量。有两种度量是在[Lines2012A]对shaplets树提出的。我们进行了全面的实验,结果表明,新度量比信息增益速度更快。
(3)在广泛的问题上,我们证明了基于shapelet转换数据的分类器比基于树的shapelet分类器更精确。
(4)我们比较了基于shapelet转换数据构造的分类器与时域构造的分类器的性能。
(5)我们通过使用后转换集群将原始shapelet转换扩展为将shapelet与问题域关联起来。
(6)我们提供了三个新的时间序列分类问题:Beetle/Fly,Bird/Chicken,和Otoliths。
背景
文章结构组织如下。第二部分介绍时间序列分类和shapelets背景。在第三部分,我们定义了可替代信息增益的三种度量方式。在第四部分,我们提出了shapelets转换算法。我们在第五部分讨论我们用于实验的数据集。在第六部分我们描述了实验设计和实验结果以及性能指标分析。最后在第七部分是我们的结论。
最初由[Ye2009A]提出的Shapelets是最大程度地预测目标变量的时间序列段。 所有可能的片段被认为是潜在的候选者,而候选者与所有训练系列的最小距离被用作辨别性特征,用于对该候选者在目标变量上的信息增益进行准确排序。其他用来评估shapeplets候选者的预测准确度的质量度量指标也已经被提了出来,例如F-Stats[Lines2012A],Kruskall-Wallis或Mood’s median[Hills2014A]。此外,一组shapelet与时间序列的最小距离可以被视为数据变换[Lines2012A],而标准分类器已经实现了对shapelet变换表示的高精度分类[Hills2014A]。
由于候选者数量很多,蛮力shapelets发现的运行时间是不可行的。因此,一系列加速技术已经被提了出来,例如早期放弃距离计算和信息增益度量的熵剪枝。其他加速依赖于计算的重用和搜索空间的剪枝,以及利用SAX表示的映射。通过阐述异常shapelets候选者的使用,训练时间也得到了削减。此外,利用GPU的基于硬件的优化也改善了shapelets的发现。Shapelets已应用于一系列实际应用中。无监督的shapelets也被用于聚类时间序列。已发现shapelets可用于通过步态数据识别人类。手势识别是另一个应用领域,它受益于shapelets的发现。在医学和健康信息学领域,辨别性的shapelets已经能用来实现对时间序列的有效早期分类。
与最先进的方法相比,我们提出了一种新方法,可以直接学习接近最优的shapelets,而无需在从时间序列段中提取的候选池中进行详尽搜索
时间序列分类
时间序列是一个数据序列,通常以固定的时间间隔按时间顺序记录。假设我们有一个n个时间序列的集合T={T1, T2, …, Tn},每个序列Ti都有m个实值,即Ti=<ti,1, ti,2, …, ti,m>,以及一个类标ci。我们假设T中的序列长度都是m,这不是必须的(参考[Hu2013A]对这个问题的讨论)。给定一个数据集T,时间序列分类问题是寻找一个从可能时间序列空间映射到可能类值空间的函数。
与所有时间序列数据挖掘一样,时间序列分类依赖于相似性度量来比较数据。相似性度量可以嵌入到分类器中,或者在分类之前通过数据转换引入。辨别性相似性特征通常分为三类:时间相似性(基于相关性),变化相似性(基于自动相关性),以及形状相似性(基于形状)。我们专注于最能捕捉形状相似性的表示。
如果函数fc描述了类c的公共形状, 那么一个时间序列可以描述为
其中si是序列i的偏移量,∈j是噪音的某种形式。形状相似可以分为全局相似和局部相似。全局形状相似性是指定义类相似性的基础形状与序列的长度大致相同,但同一类中的序列可以有不同的偏移量。因此,举个例子,函数fc可以是正玄的,
这种形式的全局相似性可以通过显式的重新排列来检测,或者,更普遍的,通过变换到频域。然而,当基于形状的相似性是局部的时,这些方法不太可行。在这种情况下,识别形状比序列小得多,并且可以出现在任何点上。例如,形状可以是嵌入在噪声中的正弦波,在短时间内随机触发。此时fc的形式如下,
其中l是形状的长度。基于全序列的傅立叶变换的技术不太可能检测到这些嵌入的形状,而基于滑动窗口的光谱包络方法是不合适的,因为我们假设l很小。Shapelets在[Ye2009A]中被介绍用来度量这种相似性。
Shapelets
一个shapelet是时间序列集合T中某条时间序列的子序列。时间序列集合T中每条时间序列的每条子序列都可以作为一个候选。shapelets是通过在最小长度和最大长度之间对每个候选者的详细搜索找到的。形状被独立标准化;由于我们感兴趣的是检测局部形状相似性,因此它们必须不随比例和偏移而变化。shapelet发现有三个主要组件:候选生成,shapelet和时间序列之间的相似性度量,以及shapelets质量的一些度量。通用的shapelets发现算法定义如算法1。
生成候选者
长度为m的时间序列包含m-l+1个长度为l的不同的候选形状。我们将序列Ti中所有长度为l的标准化的子序列的集合表示为Wi, l。数据集T中所有长度为l的子序列的集合表示为Wl={W1, l∪W2, l∪…∪Wn, l}。数据集T所有候选shapelets集合表示为W={Wmin∪Wmin+1∪…∪Wmax},其中min≥3,max≤m。W有|W|=∑_(l=min)^max▒〖n(m-l+1)〗个候选对象。
shapelet距离计算
待翻译
shapelet评估
算法1需要一个函数来评估shapelet质量。shapelet质量取决于类值V被距离DS集合分隔的程度。标准方法是使用信息增益(IG)。对DS进行排序,并对S每个可能分割点sp处的IG进行评估,其中有效分割点是DS中任意两个连续距离之间的平均值.对于每一个可能的分割点,IG是通过将DS中的所有元素进行分割,其中DS小于sp的分进AS,其他元素分进BS来计算的。分割点sp处的IG计算如下:
加速技术
因为shapelet搜索是枚举的,对于给定的长度l,都有n(m-l+1)个候选shapelets。找到一个shapelet的距离集合DS需要扫描整条的时间序列,序列距离函数的调用程序复杂度为O(m),每一次的距离计算有需要点对间的操作时间复杂度为O(l)。因此每条shapelet的时间复杂度为O(nml),而整个的搜索时间复杂度为O(n2m4)。这也是为什么对shapelets的大部分研究都集中在shapelet发现的加速技术上。三种类型的加速技术已经被提了出来。
候选序列S和时间序列Ti之间距离计算的早期放弃。因为dS, i是S和Ti之间m-l+1个距离中最小的一个,如果单个计算大于迄今为止发现的最佳值,则可以放弃这些计算。在距离计算过程中,通过将子序列归一化,以及首先对候选序列重新排序以比较最大值,可以进一步提高速度[Rakthanmanon2012A]。算法2总结了这些改进。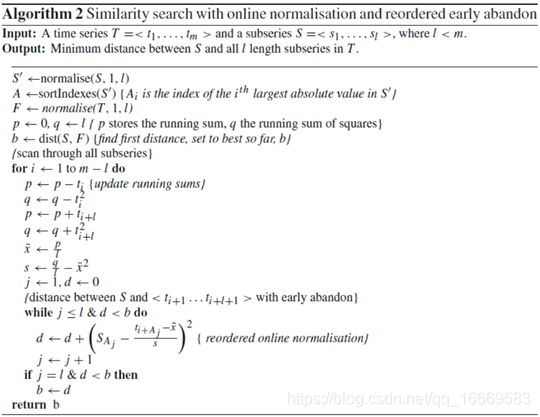
序列间距离统计的预计算。因为每个子序列都是相互比较的,所以计算中有重复。因此,举例如下,当要比较从位置a开始的子序列和从位置b开始的子序列时,许多的计算在比较从位置a-1和位置b-1开始的子序列是已经进行过了,这就出现了很多的重复计算。一种以空间换时间的方法在[Mueen2011A]中被提了出来。对于每一对序列Ti和Tj,Ti和Tj的累积和、平方和和和叉积是预先计算的。使用这些统计量,子序列间的距离能够在恒定时间内被计算出来,使得shapelets的发现算法的时间复杂度变为O(n¬¬2m3)。然而,在shapelet发现之前,所有序列之间的交叉积的预计算需要O(n2m2)内存,这对于大多数问题都是不可行的。作为替代的,Mueen等人[Mueen2011A]提出在开始扫描每个序列之前计算这些统计信息,使得内存需求降为了O(nm2),但是增加了时间开销。
Shapelet的早期放弃。一种shapelet评估的早期放弃方法在[Ye2011A]中被提了出来。在每一个dS, i的值被计算出来之后,信息增益IG的上界通过假设未来最优的分布被提了出来。如果这个上限低于迄今为止发现的最佳值,则可以放弃Ds的计算。通过放弃糟糕的shapelets,巨大的潜在速度加快了,这需要额外的一点开销来计算每个新dS, i的最佳拆分和上界。然而,对于多类问题,只有通过枚举所有可能类的拆分分配才能找到正确的上限,这会显著增加开销。
可替代的shapelet质量度量
不像shapelet树,我们的shapelet转换不需要通过质量度量找到显式拆分点。IG引入了额外的时间开销,可能不适合多类问题,因为它仅限于二进制拆分。我们研究了基于阶级人口之间距离分布差异的假设检验的替代形状质量度量。我们研究了三种不同的方法来量化类如何被距离Ds列表分割。
Kruskal-Walli
KW是一个非参数测试两个样本是否来自具有相同中值的分布[Kruskal1952A]。检验统计量是一个类内等级和全局平均等级之间的平方加权差。给定距离D的排序列表,被类成员分为D1,…Dc,以及级别列表R=<1,2,…n>,将R中Di中的元素的等级设置为Ri,KW的统计量定义如下: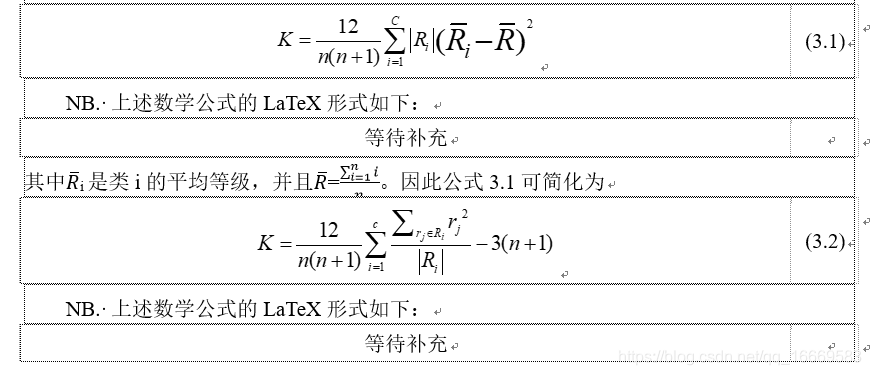
方差F统计量分析
用于方差分析的F-统计量被用来检测一个集合中C个样本的均值差的假设。原假设是是每个样本的总体平均值相同。这个假设的检验统计是组间变异与组内变异的比率。与组内变异性相比,值越高,组间变异性越大。一个高质量的shapelet与一个类的成员有小距离,与其他类的成员有大距离;因此,一个高质量的shapelet产生一个高的F-统计量。为了评估距离列表D=<d1,d2,…,dn>,我们先用类成员分割它们,即Di包含候选shapelet到第i类时间序列的距离。F-统计量shapelet质量度量公式如下:
Mood’s 中位数
Mood[Mood1974A]中位数(MM)是一种确定两个样本的中间值是否来自同一分布的非参数测试。不像IG和KW,MM不要求D排序。计算MM只需要中位数,使用Quickselect[Hoare1962A]查找中位数的时间复杂度为O(n)。中位数用于从D创建一个应急表,其中记录中间值上下每一类的计数。让oi1代表高于中位数的类i的计数,oi2代表低于中位数的类i的计数。如果零假设是真的,我们期望中间值上下的分割大致相同。如果独立性的无效假设为真,则让ei1和ei2表示在中位数之上和之下的预期观察次数。MM统计公式为:
shapelet转换
[Bagnall2012A] 证明了用集合方法将转换与分类算法分离的重要性,其中每个成员合奏是在原始数据的不同变换上构建的。它们表明,首先,在识别特征不在时间域的问题上,在不同的数据空间中操作比设计更复杂的分类器产生更大的性能改进。其次,对变换后的数据集进行基本的集成可以显著地改进简单的分类器。我们将这种直觉应用于shapelets,并将转换从分类器中分离出来。
我们的转换过程分为三个不同的阶段。首先,该算法对数据进行一次扫描,提取出最佳的K形状。k是要存储的最大shapelet数的截止值,对提取的单个shapelet的质量没有影响。其次,可以通过忽略截止点以下的shapelets(即将256个shapelets减少到10个)或通过聚集shapelets(看4.4节)来减少k shapelets集。最后,创建一个新的转换数据集,其中每个属性表示一个shapelet,该属性的值是shapelet和原始序列之间的距离。以这种方式转换数据将shapelet查找与分类分离,从而允许将转换后的数据集与任何分类器一起使用。
shapelet生成
提取k个最好的shapelets的过程定义如算法3。
该算法以类似于原始shapelet算法的方式处理数据[Ye2011A](算法1)。对于数据集中的每个序列,检查最小值和最大值之间的所有长度子序列。然而,不像算法1那样所有候选者都要进行评估然后存储最好的那个,我们的缓存算法存储给定时间序列的所有候选对象及其相关的质量度量(算法第九行)。一旦对一个序列的所有候选对象进行了评估,它们将按质量排序,并删除自相似的shapelets。自相似的shapelet取自同一序列并具有重叠索引。我们将一个序列的非自相似的shapelets集合与当前的最佳shapelets合并,并保留前面k个,迭代数据集,直到所有序列都被处理完。我们不会无限期地存储所有候选者;在处理完每个序列之后,我们只保留到目前为止属于最佳k个的那些,并丢弃所有其他shapelets。因此,我们避免了保留所有候选人所需的巨大空间开销。在处理候选者之间的自相似性时,在删除自相似shapelets之前,需要临时存储和评估单个序列中的所有候选者。这可以防止不正确地拒绝shapelets。比如,在一条给定的序列中,候选者A可能被添加到当前最好的前k个里面。如果候选者B与A重叠,并且质量更高,A就会被拒绝。如果有第三个候选者C的质量更高,且被认定为与B自相似,但是与A不相似,那么C就会替换掉B,此时被删除的候选者A原本可以成为前k个里面的有效候选者的。我们通过在删除自相似序列之前评估给定序列的所有候选序列来克服这个问题(算法3第9行)。一旦对给定序列的所有候选者进行了评估,它们将被按质量降序进行排序(第10行)。然后,可以按质量顺序对排序后的候选者集进行自相似性评估(第11行),从而始终保留最佳候选者,并安全地删除自相似候选者。
长度参数近似

原始算法和我们的缓存算法都需要两个长度参数:最小和最大。这些值定义候选shapelet长度的范围。较小的范围可以提高速度,但如果它们阻碍考虑最有用的子序列,则可能会降低精度。为了适应在一系列数据集上运行shapelet过滤器,而不需要专门了解数据,我们定义了一个简单的算法来估计最小和最大参数。
算法4中描述的过程从数据集T中随机选择十个序列作为数据子集,并使用算法3在该数据子集中找到最佳的十个shapelets的集合。对于此搜索,最小值=3,最大值设置为n。选择和搜索过程总共重复10次,生成一组100个shapelets。shapelets按长度排序,第25个shapelet的长度返回作为最小值,第75个shapelet的长度返回作为最大值。虽然这不一定会产生最佳参数,但它确实提供了一种自动方法,在多个数据集中近似最小值和最大值。因此,我们可以将过滤器与原始的shapelet树实现进行比较。
shapelet筛选
在过滤器中使用k shapelets不一定会产生最佳的分类数据。使用太少的shapelet无法向分类器提供足够的信息;使用过多可能导致过拟合,或稀释重要形状的影响。对于我们的实验,我们在过滤器中使用n/2个shapelets,其中n是单个数据序列的长度。
聚类shapelet
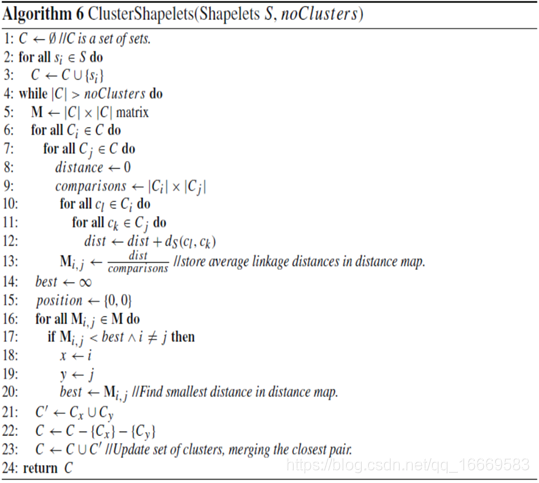
根据定义,能够很好区分类的shapelet将和一组来自同一类的其他实例的子序列相似。转换通常包括多个彼此匹配的shapelet。在某些数据集中,包含辨别性shapelet的匹配项可能意味着缺少有用的shapelets;此外,重复可以降低转换数据的可理解性。为了缓解这些问题,我们使用算法6中给出的过程对转换后的shapelets进行分层聚类。创建一个表示每对shapelet之间shapelet距离的距离映射。对于k个shapelets,这是一个在对角线周围有典型对称性的k×k矩阵(由零组成)。它们之中拥有最小shapelet距离的序对被聚类。更新后的k−1×k−1距离图是在删除聚类对并添加簇后创建的。重复该过程,直到形成用户指定数量的集群。我们计算两个簇(ci和cj)之间的shapelet距离,作为ci的每个成员和cj的每个成员之间shapelet距离的平均值。对于任何shapelets集群,我们用适当的shapelet质量度量最好的集群成员表示集群。假定集群的其他成员与此shapelet匹配。
实现代码
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import timeseriesweka.filters.shapelet_transforms.ShapeletTransform;
import static timeseriesweka.filters.shapelet_transforms.quality_measures.ShapeletQuality.ShapeletQualityChoice.INFORMATION_GAIN;
import weka.classifiers.Classifier;
import weka.classifiers.bayes.BayesNet;
import weka.classifiers.bayes.NaiveBayes;
import weka.classifiers.functions.SMO;
import weka.classifiers.lazy.IB1;
import weka.classifiers.meta.RotationForest;
import weka.classifiers.trees.J48;
import weka.classifiers.trees.RandomForest;
import weka.classifiers.trees.shapelet_trees.*;
import weka.core.Instances;
public class Hills14shapelet {
// There are two types of dataset assessment - LOOCV or Train/Test split
private enum AssesmentType{LOOCV, TRAIN_TEST};
// An array containing all the file names of the datasets used in the experiments
private static String[] fileNames={
//Number of train, test cases, length, classes
"Adiac", // 390,391,176,37
"Beef", // 30,30,470,5
"ChlorineConcentration", // 467,3840,166,3
"Coffee", // 28,28,286,2
"DiatomSizeReduction", // 16,306,345,4
"DP_Little", // 400,645,250,3
"DP_Middle", // 400,645,250,3
"DP_Thumb", // 400,645,250,3
"ECGFiveDays", // 23,861,136,2
"ElectricDevices", // 8953,7745,96,7
"FaceFour", // 24,88,350,4
"GunPoint", // 50,150,150,2
"ItalyPowerDemand", // 67,1029,24,2
"Lighting7", // 70,73,319,7
"MedicalImages", // 381,760,99,10
"MoteStrain", // 20,1252,84,2
"MP_Little", // 400,645,250,3
"MP_Middle", // 400,645,250,3
"PP_Little", // 400,645,250,3
"PP_Middle", // 400,645,250,3
"PP_Thumb", // 400,645,250,3
"SonyAIBORobotSurface", // 20,601,70,2
"Symbols", // 25,995,398,6
"SyntheticControl", // 300,300,60,6
"Trace", // 100,100,275,4
"TwoLeadECG", // 23,1139,82,2
"Herrings", // 64,64,512,2
// "Herring500", // 100,100,500,2
"SyntheticData", // 10,1000,500,2
// "Beetle-fly", // 40,40,512,2
// "Bird-chicken", // 40,40,512,2
// "ShapesAll" // 600,600,512,60
};
private static final String userPath="C:\\Users\\ajb\\Dropbox\\TSC Problems\\";
// Paths of the folders where the datasets are stored
private static String[] filePaths={
userPath+"Adiac/", // Adiac
userPath+"Beef/", // Beef
userPath+"ChlorineConcentration/", // ChlorineConcentration
userPath+"Coffee/", //Coffee
userPath+"DiatomSizeReduction/", // DiatomSizeReduction
userPath+"Bones/", // "DP_Little"
userPath+"Bones/", // "DP_Middle"
userPath+"Bones/", // "DP_Thumb"
userPath+"ECGFiveDays/", // ECGFiveDays
userPath+"ElectricDevices/", // ElectricDevices
userPath+"FaceFour/", // FaceFour
userPath+"GunPoint/", // GunPoint
userPath+"ItalyPowerDemand/", // ItalyPowerDemand
userPath+"Lighting7/", // Lighting7
userPath+"MedicalImages/", // MedicalImages
userPath+"MoteStrain/", // MoteStrain
userPath+"Bones/", // MP_Little
userPath+"Bones/", // MP_Middle
userPath+"Bones/", // PP_Little
userPath+"Bones/", // PP_Middle
userPath+"Bones/", // PP_Thumb
userPath+"SonyAIBORobotSurface/", // SonyAIBORobotSurface
userPath+"Symbols/", // Symbols
userPath+"SyntheticControl/", // SyntheticControl
userPath+"Trace/", // Trace
userPath+"TwoLeadECG/", // TwoLeadECG
userPath+"Otoliths/", // Herrings
// userPath+"Otoliths/", // Herring500
userPath+"SyntheticData/", // SyntheticData
userPath+"MPEG7Shapes/", // Beetle-fly
userPath+"MPEG7Shapes/", // Bird-chicken
// userPath+"MPEG7Shapes/" // ShapesAll
};
// An array containing the assesment type for each of the datasets.
private static AssesmentType[] assesmentTypes = {
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Adiac
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Beef
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // ChlorineConcentration
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Coffee
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // DiatomSizeReduction
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // DP_Little
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // DP_Middle
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // DP_Thumb
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // ECGFiveDays
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // ElectricDevices
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // FaceFour
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // GunPoint
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // ItalyPowerDemand
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Lighting7
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // MedicalImages
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // MoteStrain
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // MP_Little
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // MP_Middle
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // PP_Little
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // PP_Middle
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // PP_Thumb
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // SonyAIBORobotSurface
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Symbols
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // SyntheticControl
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Trace
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // TwoLeadECG
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // Herrings
AssesmentType.LOOCV, // Herring500
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST, // SyntheticData
AssesmentType.LOOCV, // Beetle-fly
AssesmentType.LOOCV, // Bird-chicken
AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST // ShapesAll
};
// An array containing the shapelet min-max interval for each of the datasets.
private static int[][] shapeletMinMax = {
{3, 10}, // Adiac
{8, 30}, // Beef
{7, 20}, // ChlorineConcentration
{18,30}, // Coffee
{7,16}, // DiatomSizeReduction
{9, 36}, // DP_Little
{15, 43}, // DP_Middle
{11, 47}, // DP_Thumb
{24, 76}, // ECGFiveDays
{10, 42}, // ElectricDevices
{20, 120}, // FaceFour
{24, 55}, // GunPoint
{7, 14}, // ItalyPowerDemand
{20, 80}, // Lighting7
{9, 35}, // MedicalImages
{16, 31}, // MoteStrain
{15, 41}, // MP_Little
{20, 53}, // MP_Middle
{13, 38}, // PP_Little
{14, 34}, // PP_Middle
{14, 41}, // PP_Thumb
{15, 36}, // SonyAIBORobotSurface
{52, 155}, // Symbols
{20, 56}, // SyntheticControl
{62, 232}, // Trace
{7, 13}, // TwoLeadECG
{30, 101}, // Herrings
{30, 101}, // Herring500
{25, 35}, // SyntheticData
{30, 101}, // Beetle-fly
{30, 101}, // Bird-chicken
{30, 110} // ShapesAll
};
// Variables for holding filters for data transformation
private static ShapeletTransform shapeletFilter;
// Variables for holding data
private static Instances[] instancesTrain;
private static Instances[] instancesTest;
// Variables for holding the classifier information
private static Classifier classifiers[];
private static String classifierNames[];
// Variables for holding user input
private static int tableToProduceIndex;
private static String outFileName;
private static int fileToProcessIndex;
private static int classifierToProcessIndex;
// Method to load the datasets.
private static void loadData(){
instancesTrain = new Instances[fileNames.length];
instancesTest = new Instances[fileNames.length];
//Load all the datasets and set class index for loaded instances
for(int i=0; i<fileNames.length; i++){
// Load test/train splits
if(assesmentTypes[i] == AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST){
instancesTrain[i] = ShapeletTransform.loadData(filePaths[i]+fileNames[i]+"_TRAIN.arff");
instancesTest[i] = ShapeletTransform.loadData(filePaths[i]+fileNames[i]+"_TEST.arff");
}else if(assesmentTypes[i] == AssesmentType.LOOCV){
instancesTrain[i] = ShapeletTransform.loadData(filePaths[i]+fileNames[i]+".arff");
instancesTest[i] = null;
}
// Set class indices
instancesTrain[i].setClassIndex(instancesTrain[i].numAttributes() - 1);
if(assesmentTypes[i] == AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST){
instancesTest[i].setClassIndex(instancesTest[i].numAttributes() - 1);
}
}
}
public static void table2() throws Exception{
// Initialise classifiers required for this experiment
classifiers = new Classifier[4];
classifiers[0] = new ShapeletTreeClassifier("infoTree.txt");
classifiers[1] = new KruskalWallisTree("kwTree.txt");
classifiers[2] = new MoodsMedianTreeWithInfoGain("mmWithInfoTree.txt");
classifiers[3] = new FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain("fStatTree.txt");
// Set up names for the classifiers - only used for output
classifierNames = new String[4];
classifierNames[0] = "IG";
classifierNames[1] = "KruskalWallis";
classifierNames[2] = "MoodMedIG";
classifierNames[3] = "F-stat";
if((classifierToProcessIndex < 1 || classifierToProcessIndex > classifiers.length) && classifierToProcessIndex != -1 ){
throw new IOException("Invalid classifier identifier.");
}else{
if(classifierToProcessIndex != -1){
classifierToProcessIndex--;
}
}
// Compute classifier accuracies for each classifier
double accuracies[][] = new double[classifiers.length][];
for(int i = 0; i < classifiers.length; i++){
if(i == classifierToProcessIndex || classifierToProcessIndex == -1){
accuracies[i] = classifierAccuracy(i, false, true, false);
}
}
// Write experiment output to file
writeFileContent(accuracies);
}
public static void table3() throws Exception{
// Initialise classifiers required for this experiment
classifiers = new Classifier[4];
classifiers[0] = new ShapeletTreeClassifier("infoTree.txt");
classifiers[1] = new FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain("fStatTree.txt");
classifiers[2] = new KruskalWallisTree("kwTree.txt");
classifiers[3] = new MoodsMedianTree("mmTree.txt");
// Set up names for the classifiers - only used for output
classifierNames = new String[4];
classifierNames[0] = "Information Gain";
classifierNames[1] = "F-stat";
classifierNames[2] = "Kruskal-Wallis";
classifierNames[3] = "Mood's Median";
if((classifierToProcessIndex < 1 || classifierToProcessIndex > classifiers.length) && classifierToProcessIndex != -1 ){
throw new IOException("Invalid classifier identifier.");
}else{
if(classifierToProcessIndex != -1){
classifierToProcessIndex--;
}
}
// Record classifier times to find single shapelet
double times[][] = new double[classifiers.length][instancesTrain.length];
for(int i = 0; i < classifiers.length; i++){
if(i == classifierToProcessIndex || classifierToProcessIndex == -1){
for(int j = 0; j < instancesTrain.length; j++){
if(fileToProcessIndex == j || fileToProcessIndex == -1){
// Get training data
Instances data = null;
if(assesmentTypes[j] == AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST){
data = instancesTrain[j];
}else if(assesmentTypes[j] == AssesmentType.LOOCV){
data = instancesTrain[j].trainCV(instancesTrain[j].numInstances(), 0);
}
// Store time
if(classifiers[i] instanceof ShapeletTreeClassifier){
times[i][j] = ((ShapeletTreeClassifier)classifiers[i]).timingForSingleShapelet(data, shapeletMinMax[j][0], shapeletMinMax[j][1]);
}else if(classifiers[i] instanceof KruskalWallisTree){
times[i][j] = ((KruskalWallisTree)classifiers[i]).timingForSingleShapelet(data, shapeletMinMax[j][0], shapeletMinMax[j][1]);
}else if(classifiers[i] instanceof MoodsMedianTree){
times[i][j] = ((MoodsMedianTree)classifiers[i]).timingForSingleShapelet(data, shapeletMinMax[j][0], shapeletMinMax[j][1]);
}else if(classifiers[i] instanceof MoodsMedianTreeWithInfoGain){
times[i][j] = ((MoodsMedianTreeWithInfoGain)classifiers[i]).timingForSingleShapelet(data, shapeletMinMax[j][0], shapeletMinMax[j][1]);
}else if(classifiers[i] instanceof FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain){
times[i][j] = ((FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain)classifiers[i]).timingForSingleShapelet(data, shapeletMinMax[j][0], shapeletMinMax[j][1]);
}
}
}
}
}
// Write experiment output to file
writeFileContent(times);
}
public static void table4_5() throws Exception{
// Initialise classifiers required for this experiment
classifiers = new Classifier[8];
classifiers[0] = new ShapeletTreeClassifier("infoTree.txt");
classifiers[1] = new J48();
classifiers[2] = new IB1();
classifiers[3] = new NaiveBayes();
classifiers[4] = new BayesNet();
classifiers[5] = new RandomForest();
classifiers[6] = new RotationForest();
classifiers[7] = new SMO();
// Set up names for the classifiers - only used for output
classifierNames = new String[8];
classifierNames[0] = "ShapeletTree";
classifierNames[1] = "C4.5";
classifierNames[2] = "1NN";
classifierNames[3] = "Naive Bayes";
classifierNames[4] = "Bayesian Network";
classifierNames[5] = "Random Forest";
classifierNames[6] = "Rotation Forest";
classifierNames[7] = "SVM (linear)";
if((classifierToProcessIndex < 1 || classifierToProcessIndex > classifiers.length) && classifierToProcessIndex != -1 ){
throw new IOException("Invalid classifier identifier.");
}else{
if(classifierToProcessIndex != -1){
classifierToProcessIndex--;
}
}
// Compute classifier accuracies for each classifier
double accuracies[][] = new double[classifiers.length][];
boolean transFlag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < classifiers.length; i++){
if(!(classifiers[i] instanceof ShapeletTreeClassifier)){
//shapeletFilter = new Shapelet();
//shapeletFilter.setQualityMeasure(Shapelet.ShapeletQualityChoice.INFORMATION_GAIN);
//shapeletFilter.supressOutput();
transFlag = true;
}
if(i == classifierToProcessIndex || classifierToProcessIndex == -1){
accuracies[i] = classifierAccuracy(i, transFlag, false, true);
}
}
// Write experiment output to file
writeFileContent(accuracies);
}
/**
* A method to validate a given classifier
*
* @param classifierIndex index of the classifier to be validated
* @param useTransformedData flag indicating what type of data to use.
* Shapelet is used for data transformation.
* @param computeErrorRate flag indicating whether error rate is required
* rather than classifier accuracy.
* @param usePercentage flag indicating whether an accuracy/error rate should
* be converted to percentage.
* @return classifier accuracy/error rate
*/
private static double[] classifierAccuracy(int classifierIndex, boolean useTransformedData, boolean computeErrorRate, boolean usePercentage){
// Array for storing the classifier accuracies
double[] accuracies = new double[instancesTrain.length];
// Generate average accuracies
for (int n = 0; n < instancesTrain.length; n++){
if(fileToProcessIndex == n || fileToProcessIndex == -1){
try{
if(assesmentTypes[n] == AssesmentType.TRAIN_TEST){
accuracies[n] = classiferAccuracyTrainTest(classifierIndex, n, useTransformedData);
}else if(assesmentTypes[n] == AssesmentType.LOOCV){
accuracies[n] = classiferAccuracyLOOCV(classifierIndex, n, useTransformedData);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(computeErrorRate){
accuracies[n] = 1 - accuracies[n];
}
if(usePercentage){
accuracies[n] *= 100;
}
}
}
return accuracies;
}
/**
* A method to perform simple train/test split validation using given classifier
* and data.
*
* @param classifierIndex index of the classifier to be used in validation.
* @param dataIndex index of the data to be used in validation.
* @param trainData data to be used to build the classifier.
* @param testData data to be used to test the classifier
* @return accuracy of the classifier.
*/
private static double classiferAccuracyTrainTest(int classifierIndex, int dataIndex, boolean useTransformedData){
double accuracy = 0.0;
Instances trainData = null, testData = null;
if(useTransformedData){
//Initialize filter
try{
shapeletFilter = ShapeletTransform.createFilterFromFile(filePaths[dataIndex]+fileNames[dataIndex]+"_TRAIN_TRANS.txt", instancesTrain[dataIndex].numAttributes()/2);
shapeletFilter.supressOutput();
}catch (Exception e){
shapeletFilter = new ShapeletTransform();
shapeletFilter.setQualityMeasure(INFORMATION_GAIN);
shapeletFilter.supressOutput();
shapeletFilter.setNumberOfShapelets(instancesTrain[dataIndex].numAttributes()/2);
shapeletFilter.setShapeletMinAndMax(shapeletMinMax[dataIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataIndex][1]);
shapeletFilter.setLogOutputFile(filePaths[dataIndex]+fileNames[dataIndex]+"_TRAIN_TRANS.txt");
}
//Transform data
try{
trainData = shapeletFilter.process(instancesTrain[dataIndex]);
testData = shapeletFilter.process(instancesTest[dataIndex]);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
trainData = instancesTrain[dataIndex];
testData = instancesTest[dataIndex];
}
// Build classifer using train split
buildClassifier(classifierIndex, trainData, dataIndex);
//Classify test instancs while recording accuracy
for(int j = 0; j < testData.numInstances(); j++){
double classifierPrediction = 0.0;
try{
classifierPrediction = classifiers[classifierIndex].classifyInstance(testData.instance(j));
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
double actualClass = testData.instance(j).classValue();
if(classifierPrediction == actualClass) {
accuracy++;
}
// Compute average accuracy if it is the last test instance
if(j == testData.numInstances() - 1){
accuracy /= testData.numInstances();
}
}
return accuracy;
}
/**
* A method to perform leave one out cross validation using given classifier and
* data.
*
* @param classifierIndex index of the classifier to be used in cross validation.
* @param dataIndex index of the data to be used in cross validation.
* @param data data to be used in cross validation.
* @return accuracy of the classifier.
*/
private static double classiferAccuracyLOOCV(int classifierIndex, int dataIndex, boolean useTransformedData){
//Variables for holding folds
Instances data = instancesTrain[dataIndex];
Instances trainFold;
Instances testFold;
double accuracy = 0.0;
//Generate average accuracies
for (int n = 0; n < data.numInstances(); n++) {
System.out.println("\n\n\n\n\nProcessing fold: " + n+"\n\n\n\n\n");
//Generate folds
trainFold = data.trainCV(data.numInstances(), n);
testFold = data.testCV(data.numInstances(), n);
if(useTransformedData){
//Initialize filter
try{
shapeletFilter = ShapeletTransform.createFilterFromFile(filePaths[dataIndex]+fileNames[dataIndex]+"_TRANS_"+n+".txt", instancesTrain[dataIndex].numAttributes()/2);
shapeletFilter.supressOutput();
}catch (Exception e){
shapeletFilter = new ShapeletTransform();
shapeletFilter.setQualityMeasure(INFORMATION_GAIN);
shapeletFilter.supressOutput();
shapeletFilter.setNumberOfShapelets(instancesTrain[dataIndex].numAttributes()/2);
shapeletFilter.setShapeletMinAndMax(shapeletMinMax[dataIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataIndex][1]);
shapeletFilter.setLogOutputFile(filePaths[dataIndex]+fileNames[dataIndex]+"_TRANS_"+n+".txt");
}
//Transform data
try{
trainFold = shapeletFilter.process(trainFold);
testFold = shapeletFilter.process(testFold);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Build classifer using train fold
buildClassifier(classifierIndex, trainFold, dataIndex);
double classifierPrediction = 0.0;
try{
classifierPrediction = classifiers[classifierIndex].classifyInstance(testFold.instance(0));
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
double actualClass = testFold.instance(0).classValue();
if(classifierPrediction == actualClass) {
accuracy++;
}
// Compute average accuracy if it is the last test instance
if(n == data.numInstances() - 1){
accuracy /= data.numInstances();
}
}
return accuracy;
}
/**
* A method to build a classifier with given data.
*
* @param classifierID classifier ID, which determines which classifier is built.
* @param instances data to be used for building the classifier
* @param dataSetIndex data set index, which determines what parameters are used
* for building the classifier.
*/
private static void buildClassifier(int classifierIndex, Instances instances, int dataSetIndex){
// Set the shapelet min/max if the current classifer is a ShapeletTree or its variation
if(classifiers[classifierIndex] instanceof ShapeletTreeClassifier){
((ShapeletTreeClassifier)classifiers[classifierIndex]).setShapeletMinMaxLength(shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][1]);
}else if(classifiers[classifierIndex] instanceof KruskalWallisTree){
((KruskalWallisTree)classifiers[classifierIndex]).setShapeletMinMaxLength(shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][1]);
}else if(classifiers[classifierIndex] instanceof MoodsMedianTree){
((MoodsMedianTree)classifiers[classifierIndex]).setShapeletMinMaxLength(shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][1]);
}else if(classifiers[classifierIndex] instanceof MoodsMedianTreeWithInfoGain){
((MoodsMedianTreeWithInfoGain)classifiers[classifierIndex]).setShapeletMinMaxLength(shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][1]);
}else if(classifiers[classifierIndex] instanceof FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain){
((FStatShapeletTreeWithInfoGain)classifiers[classifierIndex]).setShapeletMinMaxLength(shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][0], shapeletMinMax[dataSetIndex][1]);
}
//Build classifier
try{
classifiers[classifierIndex].buildClassifier(instances);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* A method to write content to a given file.
*
* @param fileName file name including extension
* @param content content of the file
*/
private static void writeFileContent(double content[][]){
// Check if file name is provided.
if(outFileName == null || outFileName.isEmpty()){
outFileName = "Table_" + tableToProduceIndex +
"_File_" + (fileToProcessIndex+1) +
"_Classifier_" + (classifierToProcessIndex+1) + ".csv";
}
// If a file with given name does not exists then create one and print
// the header to it, which inlcudes all the classifier names used in the
// experiment.
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if(!isFileExists(outFileName)){
sb.append("Data Set, ");
for(int i = 0; i < classifierNames.length; i++){
if(i == classifierToProcessIndex || classifierToProcessIndex == -1){
sb.append(classifierNames[i]);
}
if(-1 == classifierToProcessIndex && i != classifierNames.length - 1){
sb.append(", ");
}
}
writeToFile(outFileName, sb.toString(), false);
}
// Print the experiment results to the file.
sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < fileNames.length; i++){
if(fileToProcessIndex == i || fileToProcessIndex == -1){
for(int k = 0; k < classifiers.length; k++){
if(k == 0){
sb.append(fileNames[i]);
sb.append(", ");
}
if(k == classifierToProcessIndex || classifierToProcessIndex == -1 ){
sb.append(content[k][i]);
}
if(-1 == classifierToProcessIndex && k != classifiers.length - 1){
sb.append(", ");
}
}
}
}
writeToFile(outFileName, sb.toString(), true);
}
/**
* A method to write text into a file.
* @param filename file name including the extension.
* @param text content to be written into the file.
* @param append flag indicating whether a file should be appended (true) or
* replaced (false).
*/
private static void writeToFile(String filename, String text, boolean append) {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
try {
//Construct the BufferedWriter object
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filename, append));
//Start writing to the output stream
bufferedWriter.write(text);
bufferedWriter.newLine();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//Close the BufferedWriter
try {
if (bufferedWriter != null) {
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* A method to check if file with a given name exists.
*
* @param filename file name including the extension.
* @return true if file with given file name exists, otherwise false.
*/
private static boolean isFileExists(String filename){
File f = new File(filename);
if(f.isFile() && f.canWrite()) {
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
tableToProduceIndex = 2;
// Process user input
try{
tableToProduceIndex = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
outFileName = args[1];
fileToProcessIndex = Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
classifierToProcessIndex = Integer.parseInt(args[3]);
// Check if file index is correct
if(fileToProcessIndex < 1 || fileToProcessIndex > fileNames.length){
throw new IOException("Invalid file identifier.");
}else{
fileToProcessIndex--; // indexed from 1 when using arguments
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.err.println("Invalid user input. Using default values");
tableToProduceIndex = 2; // refer to paper for indices
fileToProcessIndex = 0; // indexed from 0 if setting here.
classifierToProcessIndex = -1; // -1 all classifiers
}
loadData();
try{
switch (tableToProduceIndex){
case 2: table2(); break;
case 3: table3(); break;
case 4: table4_5(); break;
case 5: table4_5(); break;
default: throw new IOException("Unknow table identifier.");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)