【YOLO】训练自己的数据集(不定时更新)
引言截至2021年1月份,YOLOv5已经更新了四个版本了,如下图所示:可以根据自己的需求选择不同的版本:官网连接:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov51 数据集准备数据集的树形框架如下图所示:上述data文件夹和xml_2_txt.py文件放在yolov5的项目文件中:如上图:Annotations:用labelimg标注软件生成的.xml文件images:
YOLO系列训练自己的数据集
引言
笔者YOLO专栏链接🔗导航:
笔者更新日期 : 2025.5.5
官方链接🔗:
YOLO11指导官方文档:https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolo11/
YOL011代码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
1 数据集准备
1.1 数据集标签检查
在构建数据集前,需要对人工标注的标签进行检查,确保无误!
脚本名称:check_label.py
"""
2025.05.05
author:alian
# 0.检查目标标签
# 1.训练库修改中文路径
# 2.修改目标标签
# 3.删除xml目标
# 4.合并xml目标
"""
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import glob
from pathlib import Path
# 0.检查目标标签
def check_label(xml_dir,label_list=None):
xmls_path = glob.glob('%s/*.xml' % (xml_dir))
error_info={}
label_info = []
for xml in xmls_path:
tree = ET.ElementTree(file=xml) # 打开xml文件,送到tree解析
root = tree.getroot() # 得到文档元素对象
for label in root.iter("name"):
if label.text not in label_info:
label_info.append(label.text) # 原始标签
if label_list!=None and label.text not in label_list:
error_info[xml]=label.text # 错误标签
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write(xml)
if len(error_info)==0:
print('检查完毕,标签全部正确!')
print(label_info)
else:
print('存在以下错误标签:')
print(error_info)
# 1.修改路径
def change_path(xml_dir): # ------------------------------------------------------------------------
xmls_path = glob.glob('%s/*.xml' % (xml_dir))
for xml in xmls_path:
tree = ET.ElementTree(file=xml) # 打开xml文件,送到tree解析
root = tree.getroot() # 得到文档元素对象
old_path = Path(root.find('path').text).as_posix()
ele = old_path.split('/')[-1]
if ele.endswith('.jpg'):
root.find('path').text = xml.replace('Annotations','images').replace('.xml','.jpg')
else:
root.find('path').text = xml.replace('Annotations', 'images').replace('.xml', '.JPG')
tree=ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write(xml)
# 2.修改目标标签,若修改多个标签,则列表中的标签名要一一对应----------------------------------
def change_label(xml_dir,oldname_list,newname_list):
xmls_path = glob.glob('%s/*.xml'%(xml_dir))
for xml in xmls_path:
tree = ET.ElementTree(file=xml) # 打开xml文件,送到tree解析
root = tree.getroot() # 得到文档元素对象
for label in root.iter("name"):
for i in range(len(oldname_list)):
if label.text == oldname_list[i]:
print('%s --> %s'%(label.text,newname_list[i]))
label.text = newname_list[i]
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write(xml)
# 3.删除指定目标---------------------------------------------------------------------
def del_xmlobj(xml_path,del_classes): # 删除xml文件中的指定元素
# tree = ET.ElementTree(file=xml_path)
tree = ET.parse(xml_path) # 获得树
root = tree.getroot() # 获得其根
for object in root.findall('object'):
obj_name = object.find("name").text
if obj_name in del_classes:
root.remove(object)
tree.write(xml_path) # 修改后重新保存
def func_del(dir_path,del_classes):
for path in glob.glob('%s/*.xml'%dir_path):
del_xmlobj(path,del_classes)
# 4.将两个或多个同名的xml文件进行目标合并--------------------------------------------------------
def merge_xmlobj(xml_path1,xml_path2):
tree1 = ET.parse(xml_path1) # 获得树
root1 = tree1.getroot() # 获得其根
tree2 = ET.parse(xml_path2)
root2 = tree2.getroot()
ele_list = []
# 重复性判断(避免重复增加同一个目标)
for ele2 in root2.iter('object'):
dis = 0
num = 0
for ele1 in root1.iter('object'):
num+=1
if not iter_equal(ele1.find('bndbox'),ele2.find('bndbox')):
dis+=1
else:
break
if dis == num:
ele_list.append(ele2)
root1.extend(ele_list)
tree1.write(xml_path1)
def iter_equal(items1, items2): # 判断两个迭代器的内容是否相同
'''`True` if iterators `items1` and `items2` contain equal items.'''
if (items1.find('xmin').text == items2.find('xmin').text) \
and (items1.find('xmax').text == items2.find('xmax').text) \
and (items1.find('ymin').text == items2.find('ymin').text) \
and (items1.find('ymax').text == items2.find('ymax').text):
return True
else:
return False
def func_merge(dir_path1,dir_path2):
for path in glob.glob('%s/*.xml'%dir_path1):
path2 = path.replace(dir_path1,dir_path2)
if path2 in glob.glob('%s/*.xml'%dir_path2):
merge_xmlobj(path,path2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# xml_dir = '/data3/205b/Alian/yolov5/Customdata/subway/xml'
xml_dir = '/media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/labels_xml'
# 0.标签检查
label_list = ['Pedestrian', 'Cube', 'Pyramid', 'Sphere']
check_label(xml_dir,label_list)
# 1.训练库修改中文路径
# change_path(xml_dir)
# 2.修改目标标签
# oldname_list = ['person'] # 旧标签
# newname_list = ['Pedestrian'] # 新标签
# change_label(xml_dir, oldname_list, newname_list)
# 3.删除xml目标
# del_classes = ['Bracket'] #['Wallfitting', 'Distributionpanel', 'Advertisingboard', 'Balise', 'Sign'] # 要删除的目标
# func_del(xml_dir,del_classes)
# 4.合并xml目标
# func_merge(r'E:\Alian\yolov5\yolov5-alian\datasets\Facilities1981\22',
# r'E:\Alian\yolov5\yolov5-alian\datasets\Facilities1981\11')
1.2 标签转换(归一化)
脚本名称:xml2txt.py
"""
2025.05.05
author:alian
function: xml to txt
多种数据集并存放入data数据库中
-data
-datasets(object1)
-labels
-images
-datasets(object2)
-labels
-images
-datasets(object3)
-...
"""
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import shutil
import os, glob
class XMLToTxtConverter:
def __init__(self, dataset_path, classes):
"""
初始化转换器
:param dataset_path: 数据集路径
:param classes: 类别列表
"""
self.dataset_path = dataset_path
self.classes = classes
self.labels_xml_dir = os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "labels_xml/")
# 创建labels目录(如果存在则先删除)
self.labels_dir = os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "labels/")
if os.path.exists(self.labels_dir):
shutil.rmtree(self.labels_dir)
os.makedirs(self.labels_dir)
@staticmethod
def convert(size, box):
"""
坐标信息归一化至0-1
:param size: 图片尺寸 (width, height)
:param box: 边界框坐标 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
:return: 归一化后的坐标 (x_center, y_center, width, height)
"""
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(self, image_id):
"""
转换单个XML文件为TXT格式
:param image_id: 图片ID(不带扩展名)
"""
xml_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "labels_xml", f"{image_id}.xml")
txt_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "labels", f"{image_id}.txt")
with open(xml_path, 'r') as in_file, open(txt_path, 'w') as out_file:
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in self.classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = self.classes.index(cls) # 类别序号
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = self.convert((w, h), b) # 归一化
out_file.write(f"{cls_id} {' '.join([str(a) for a in bb])}\n")
def process_dataset(self):
"""
处理整个数据集
"""
for path in glob.glob('%s/*.xml'%(self.labels_xml_dir)):
image_id = os.path.basename(path)[:-4]
self.convert_annotation(image_id)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用示例
dataset_path = "/media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/suzhou2030" # 数据集名称
classes = ['Pedestrian'] # 类别列表
converter = XMLToTxtConverter(dataset_path, classes)
converter.process_dataset()
print(f"数据集 {os.path.basename(dataset_path)} 转换完成!")
1.3 数据集划分
根据源码的数据读取代码,数据集的目录结构可以分为以下两种:
def get_img_files(self, img_path):
"""
Read image files from the specified path.
Args:
img_path (str | List[str]): Path or list of paths to image directories or files.
Returns:
(List[str]): List of image file paths.
Raises:
FileNotFoundError: If no images are found or the path doesn't exist.
"""
try:
f = [] # image files
for p in img_path if isinstance(img_path, list) else [img_path]:
p = Path(p) # os-agnostic
if p.is_dir(): # dir---------------------1 读取目录
f += glob.glob(str(p / "**" / "*.*"), recursive=True)
# F = list(p.rglob('*.*')) # pathlib
elif p.is_file(): # file------------------------2 读取文件
with open(p, encoding="utf-8") as t:
t = t.read().strip().splitlines()
parent = str(p.parent) + os.sep
f += [x.replace("./", parent) if x.startswith("./") else x for x in t] # local to global path
# F += [p.parent / x.lstrip(os.sep) for x in t] # local to global path (pathlib)
else:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"{self.prefix}{p} does not exist")
im_files = sorted(x.replace("/", os.sep) for x in f if x.split(".")[-1].lower() in IMG_FORMATS)
# self.img_files = sorted([x for x in f if x.suffix[1:].lower() in IMG_FORMATS]) # pathlib
assert im_files, f"{self.prefix}No images found in {img_path}. {FORMATS_HELP_MSG}"
except Exception as e:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"{self.prefix}Error loading data from {img_path}\n{HELP_URL}") from e
if self.fraction < 1:
im_files = im_files[: round(len(im_files) * self.fraction)] # retain a fraction of the dataset
check_file_speeds(im_files, prefix=self.prefix) # check image read speeds
return im_files
1.3.1 目录结构一
特点:对于数据集的划分用train和val文件夹
数据集的树形框架如下图所示:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1.准备数据集(树形框架)
|-Customdata(数据库:包含不同场景下的多种数据集)
|-datasets(objects1) # 针对某一目标或者某一场景下的多目标
|-labels_xml # 原始标签xml文件
|-images # 原始图像
|-train
|-val
|-labels # 标签
|-train
|-val
|-datasets(objects2) # 第2类数据集……第n类数据集(不同场景下可能需要构建多个数据集)
……
|-divide_xml.py # 训练时划分训练集和验证集
|-data.yaml # 配置训练的数据读取
|-xml2txt.py # 脚本xml文件转换成txt文件,自动生成无需创建
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
对应的data.yaml
# yolov11
#path: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/images # 数据集所在路径 也可使用绝对路径
train: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/images/train # 索引文件所在的路径
val: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/images/val # 索引文件所在的路径
nc: 1
# Classes
names: ['Pedestrian']
安装必要库
python -m pip install scikit-learn
脚本名称divide_data_v1.py
import os
import shutil
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class DatasetSplitter:
def __init__(self, img_path, txt_path, val_size=0.2, postfix='jpg', random_state=0):
"""
初始化数据集划分器
:param img_path: 图片文件夹路径
:param txt_path: 标签文件夹路径
:param val_size: 验证集比例
:param postfix: 图片文件后缀名
:param random_state: 随机种子
"""
self.img_path = img_path
self.txt_path = txt_path
self.val_size = val_size
self.postfix = postfix
self.random_state = random_state
# 创建输出文件夹路径
self.output_train_img = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(img_path), 'images/train')
self.output_val_img = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(img_path), 'images/val')
self.output_train_txt = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(txt_path), 'labels/train')
self.output_val_txt = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(txt_path), 'labels/val')
def create_output_folders(self):
"""创建输出文件夹"""
os.makedirs(self.output_train_img, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(self.output_val_img, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(self.output_train_txt, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(self.output_val_txt, exist_ok=True)
def split_dataset(self):
"""
划分数据集并复制文件到相应目录
:return: 训练集和验证集的文件列表
"""
# 获取所有txt文件列表
txt_files = [f for f in os.listdir(self.txt_path) if f.endswith('.txt')]
# 划分训练集和验证集
train_files, val_files = train_test_split(
txt_files,
test_size=self.val_size,
shuffle=True,
random_state=self.random_state
)
return train_files, val_files
def copy_files(self, file_list, img_dest, txt_dest):
"""
复制文件到目标目录
:param file_list: 文件列表
:param img_dest: 图片目标目录
:param txt_dest: 标签目标目录
"""
for file in file_list:
# 构造源文件路径
base_name = os.path.splitext(file)[0]
img_source = os.path.join(self.img_path, f'{base_name}.{self.postfix}')
txt_source = os.path.join(self.txt_path, file)
# 构造目标文件路径
img_destination = os.path.join(img_dest, f'{base_name}.{self.postfix}')
txt_destination = os.path.join(txt_dest, file)
# 复制文件
shutil.copy(img_source, img_destination)
shutil.copy(txt_source, txt_destination)
def run(self):
"""执行数据集划分"""
print("开始划分数据集...")
self.create_output_folders()
train_files, val_files = self.split_dataset()
print(f"复制训练集文件 ({len(train_files)} 个样本)...")
self.copy_files(train_files, self.output_train_img, self.output_train_txt)
print(f"复制验证集文件 ({len(val_files)} 个样本)...")
self.copy_files(val_files, self.output_val_img, self.output_val_txt)
print(f"数据集划分完成!训练集: {len(train_files)} 个样本, 验证集: {len(val_files)} 个样本")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 配置参数
config = {
'img_path': '/media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/suzhou2030/images',
'txt_path': '/media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/suzhou2030/labels',
'val_size': 0.2,
'postfix': 'jpg',
'random_state': 0
}
# 创建并运行数据集划分器
splitter = DatasetSplitter(**config)
splitter.run()
1.3.2 目录结构二
特点:对于数据集的划分用train.txt和val.txt来进行索引
数据集的树形框架如下图所示:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1.准备数据集(树形框架)
|-Customdata(数据库:包含不同场景下的多种数据集)
|-datasets(objects1) # 针对某一目标或者某一场景下的多目标
|-labels_xml # 原始标签xml文件
|-images # 原始图像
|-labels # xml转换后的txt文件
|-datasets(objects2) # 第2类数据集……第n类数据集(不同场景下可能需要构建多个数据集)
……
|-train.txt # 数据路径索引
|-test.txt # 数据路径索引
|-divide_xml.py # 训练时划分训练集和验证集
|-data.yaml # 配置训练的数据读取
|-xml2txt.py # 脚本xml文件转换成txt文件,自动生成无需创建
|-xml2txt.py # 脚本xml文件转换成txt文件,自动生成无需创建
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
对应的data.yaml
# yolov11
#path: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/images # 数据集所在路径 也可使用绝对路径
train: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/train.txt # 索引到train.txt(包含路径索引)
val: /media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/dingjiatan_3600/val.txt # 索引到的val.txt
nc: 1
# Classes
names: ['Pedestrian']
脚本名称divide_data_v2.py
"""
2025.5.5
author: alian
功能:将数据集划分为训练集和验证集(不包含测试集)
"""
import os
import random
from typing import List
class DatasetSplitter:
def __init__(self, dataset_name: str, train_ratio: float = 0.8, random_seed: int = None):
"""
初始化数据集划分器
Args:
dataset_name: 数据集名称/路径
train_ratio: 训练集比例 (默认0.8)
random_seed: 随机种子 (保证可复现性)
"""
self.dataset_name = dataset_name
self.train_ratio = train_ratio
self.random_seed = random_seed
# 路径设置
self.images_dir = os.path.join(dataset_name, 'images')
self.train_txt = os.path.join(dataset_name, 'train.txt')
self.val_txt = os.path.join(dataset_name, 'val.txt')
# 初始化随机种子
if random_seed is not None:
random.seed(random_seed)
def get_image_list(self) -> List[str]:
"""获取图片文件列表"""
if not os.path.exists(self.images_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"图片目录不存在: {self.images_dir}")
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(self.images_dir) if f.lower().endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png'))]
if not image_files:
raise ValueError(f"未在 {self.images_dir} 中找到图片文件")
return sorted(image_files)
def split_indices(self, total: int) -> tuple:
"""
划分训练集和验证集索引
Args:
total: 总样本数
Returns:
(train_indices, val_indices)
"""
indices = list(range(total))
num_train = int(total * self.train_ratio)
train_indices = random.sample(indices, num_train)
val_indices = [i for i in indices if i not in train_indices]
return train_indices, val_indices
def write_split_files(self, image_files: List[str], train_indices: List[int], val_indices: List[int]):
"""写入划分结果到文件"""
with open(self.train_txt, 'w') as ftrain, open(self.val_txt, 'w') as fval:
for idx, img_file in enumerate(image_files):
line = f"./images/{img_file}\n"
if idx in train_indices:
ftrain.write(line)
else:
fval.write(line)
def run(self):
"""执行数据集划分"""
print(f"开始划分数据集: {self.dataset_name}")
# 获取图片列表
image_files = self.get_image_list()
total = len(image_files)
print(f"找到 {total} 张图片")
# 划分索引
train_indices, val_indices = self.split_indices(total)
print(f"训练集: {len(train_indices)} 张图片, 验证集: {len(val_indices)} 张图片")
# 写入文件
self.write_split_files(image_files, train_indices, val_indices)
print(f"划分结果已保存到: {self.train_txt} 和 {self.val_txt}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 配置参数
config = {
'dataset_name': 'suzhou2030', # 数据集名称/路径
'train_ratio': 0.8, # 训练集比例
'random_seed': 42 # 随机种子 (None表示不固定)
}
# 创建并运行数据集划分器
splitter = DatasetSplitter(**config)
splitter.run()
2 模型训练
预训练权重下载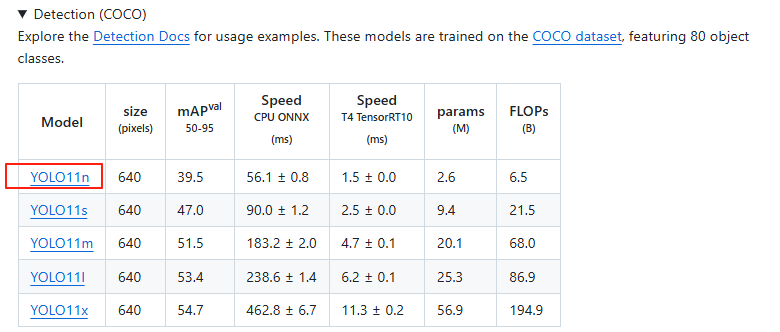
2.1 快速体验demo
以下例子统一的导入库
import os,glob
import cv2
from ultralytics import RTDETR,YOLOE,YOLO
from ultralytics.models.yolo.yoloe import YOLOEPESegTrainer
from typing import Optional, Union, List, Dict
2.1.1 模型训练
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1.训练----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 加载模型配置文件
model = YOLO(model='ultralytics/cfg/models/11/yolo11s.yaml')
# model = RTDETR(model='ultralytics/cfg/models/rt-detr/rtdetr-resnet50.yaml')
# model = YOLOE(model='xxx.yaml')
# 加载预训练模型
# model.load('yolo11s.pt')
# 模型训练
model.train(data='data.yaml', epochs=100, batch=16, device='1', imgsz=640, workers=8,cache=True,
amp=False, project='runs/train', name='0523_yolo11s',exist_ok=True)
具体的训练参数配置看官网说明:https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/train/
2.1.2 模型验证
# 2. 验证----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt") # load an official model
model = YOLO("path/to/best.pt") # load a custom model
# Validate the model
metrics = model.val() # no arguments needed, dataset and settings remembered
metrics.box.map # map50-95
metrics.box.map50 # map50
metrics.box.map75 # map75
metrics.box.maps # a list contains map50-95 of each category
具体的验证参数配置看官网说明:https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/val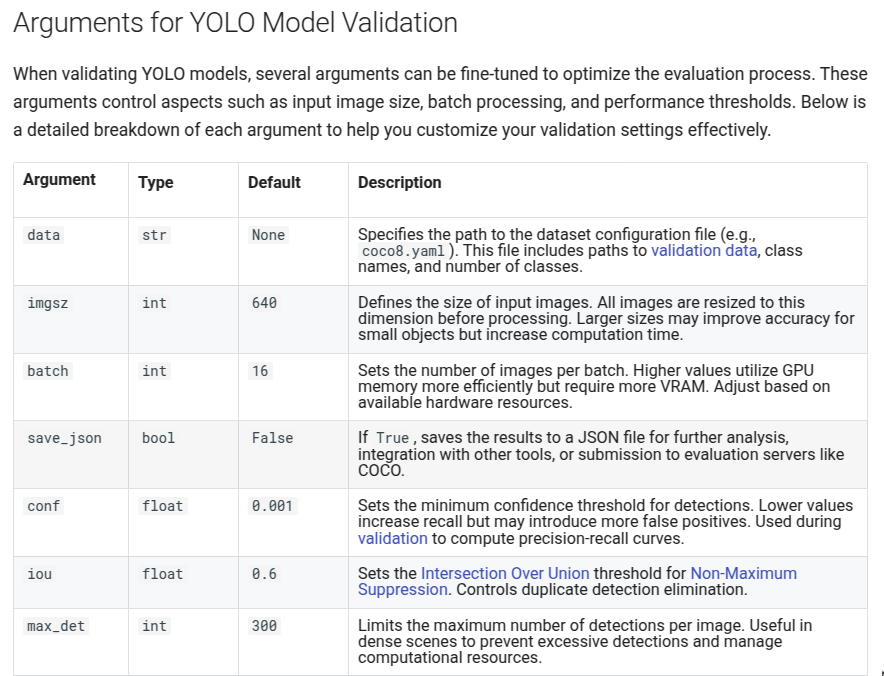
2.1.3 模型推理
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 3. 推理----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
model = YOLO(model='runs/train/0519_yolo8s/weights/best.pt') # 加载训练好的权重
source_dir = "/media/jd/4997BB1603CFE2C4/lianlirong/DATASETS/rail2d/view_test"
# 进行预测
for source in glob.glob('%s/*.jpg'%source_dir):
results = model.predict(source=source,
device='0',
imgsz=640,
conf = 0.45,
save = True,
project='runs/detect/',
name='yolov8',
exist_ok=True,
save_txt=True)
# 处理返回的结果
result = results[0]
if len(result.boxes.cls)>0:
boxes = result.boxes.xyxy # 获取边界框信息
cls = result.boxes.cls # 获取类别索引
conf = result.boxes.conf # 获取置信度
orig_shape = result.boxes.orig_shape
path = result.path
names = result.names
# result.show() # display to screen
# result.save(filename="result.jpg") # save to disk
具体的推理参数配置看官网说明:https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/predict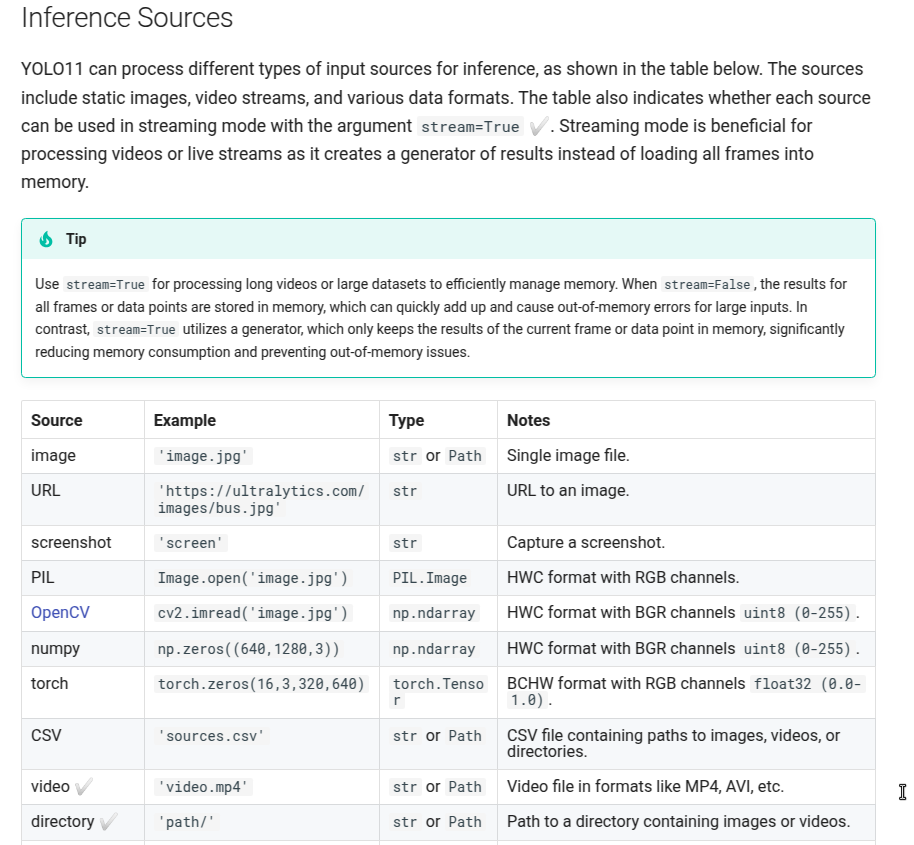
2.1.4 模型导出
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt") # load an official model
model = YOLO("path/to/best.pt") # load a custom trained model
# Export the model
model.export(format="onnx")
具体的导出参数配置看官网说明:https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export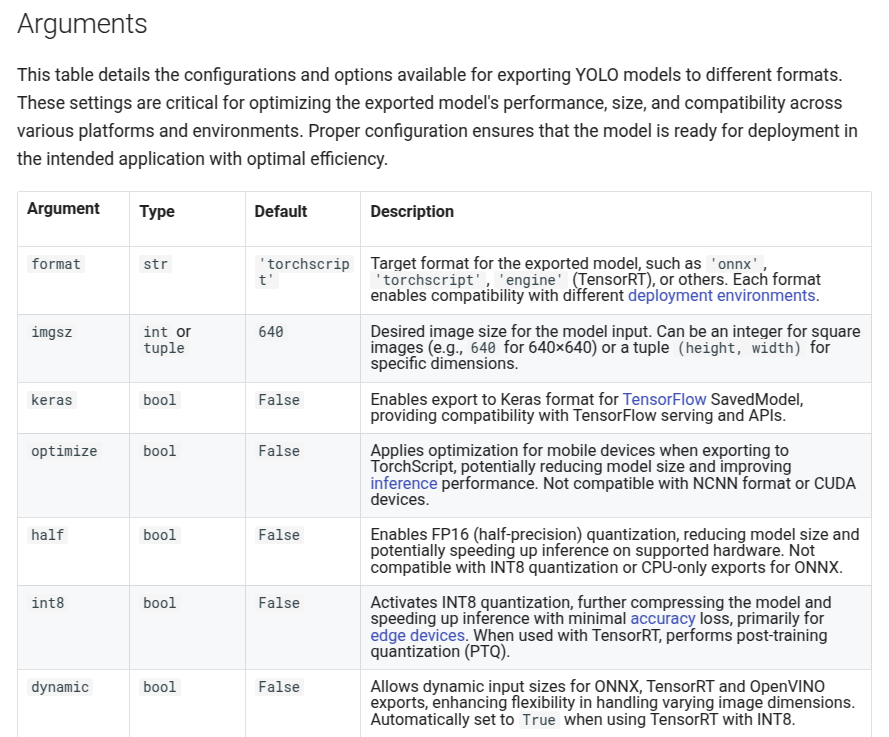
2.2 自动标注
根据模型的检测信息写入labelimg的标注信息
"""
2025.05.11
author: alian
根据YOLOv11检测结果实现自动标注(VOC格式XML)
"""
import os
import glob
import cv2
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from xml.dom import minidom
from ultralytics import YOLO
from typing import List, Dict
def create_voc_xml(image_path: str, boxes: List, cls: List, names: Dict, save_dir: str) -> None:
"""创建VOC格式的XML标注文件"""
# 确保保存目录存在
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 解析图像信息
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
height, width, depth = img.shape
# 创建XML根节点
annotation = ET.Element("annotation")
# 添加基本信息
folder = ET.SubElement(annotation, "folder")
folder.text = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(image_path)) or "."
filename = ET.SubElement(annotation, "filename")
filename.text = os.path.basename(image_path)
path = ET.SubElement(annotation, "path")
path.text = os.path.abspath(image_path)
source = ET.SubElement(annotation, "source")
database = ET.SubElement(source, "database")
database.text = "Unknown"
# 添加图像尺寸信息
size = ET.SubElement(annotation, "size")
ET.SubElement(size, "width").text = str(width)
ET.SubElement(size, "height").text = str(height)
ET.SubElement(size, "depth").text = str(depth)
ET.SubElement(annotation, "segmented").text = "0"
# 添加每个检测对象
for box, class_id in zip(boxes, cls):
obj = ET.SubElement(annotation, "object")
ET.SubElement(obj, "name").text = names[int(class_id)]
ET.SubElement(obj, "pose").text = "Unspecified"
ET.SubElement(obj, "truncated").text = "0"
ET.SubElement(obj, "difficult").text = "0"
bndbox = ET.SubElement(obj, "bndbox")
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = map(int, box.tolist())
ET.SubElement(bndbox, "xmin").text = str(xmin)
ET.SubElement(bndbox, "ymin").text = str(ymin)
ET.SubElement(bndbox, "xmax").text = str(xmax)
ET.SubElement(bndbox, "ymax").text = str(ymax)
# 格式化输出XML
xml_str = ET.tostring(annotation, encoding="utf-8")
dom = minidom.parseString(xml_str)
pretty_xml = dom.toprettyxml(indent=" ")
# 保存XML文件(与图片同名)
xml_filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))[0] + ".xml"
xml_path = os.path.join(save_dir, xml_filename)
with open(xml_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(pretty_xml)
print(f"Saved annotation to {xml_path}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 初始化模型
model = YOLO(model='yolo11n.pt')
# 配置路径
source_dir = "ultralytics/assets"
xml_save_dir = 'ultralytics/assets'
# 处理每张图片
for image_path in glob.glob(f'{source_dir}/*.jpg'):
# 进行预测
results = model.predict(
source=image_path,
device='0',
imgsz=640,
conf=0.45,
project='runs/detect/',
name='exp',
exist_ok=True,
save_txt=False # 我们不保存YOLO格式的txt
)
# 处理结果
result = results[0]
if len(result.boxes) > 0:
create_voc_xml(
image_path=image_path,
boxes=result.boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy(),
cls=result.boxes.cls.cpu().numpy(),
names=result.names,
save_dir=xml_save_dir
)
else:
print(f"No objects detected in {image_path}")
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)