【仓颉开发HarmonyOS系列】仓颉网络请求功能封装
摘要:本文介绍了在HarmonyOS中使用仓颉网络请求的方法和工具封装。重点讲解了net.http和ohos.net.http模块,前者支持客户端/服务端编程,后者提供了HTTP请求功能。文章通过示例代码展示了如何构建HTTP服务、发起POST请求等操作,并详细说明了HttpRequestOptions类的配置参数。该工具封装了网络请求的核心流程,包括请求构造、响应处理和异常管理,为Harmony
背景
在万物互联的智能时代,应用的核心价值往往依赖于与外部世界的实时交互:社交软件需要通过网络同步消息,电商应用依赖接口获取商品与订单数据,智能助手依靠API调用大模型能力,甚至系统级的设备协同也需通过网络传递指令。可以说,网络接口是连接应用与外部服务的“数字神经”,其稳定性、效率与易用性直接影响用户体验与开发效率。从技术角度看,网络接口是应用与远程服务器(或本地网络服务)交换数据的标准化通道,承载着数据请求(如GET/POST)、响应处理(如JSON/XML解析)、状态管理(如超时/重试)等关键功能。无论是简单的天气查询(调用气象API)、复杂的分布式任务调度(跨设备数据同步),还是用户身份认证(Token校验)、文件上传下载(如图片/视频传输),本质上都是通过网络接口完成“请求-响应”的闭环。本文介绍在HarmonyOS 场景中仓颉网络请求的使用和工具的封装。
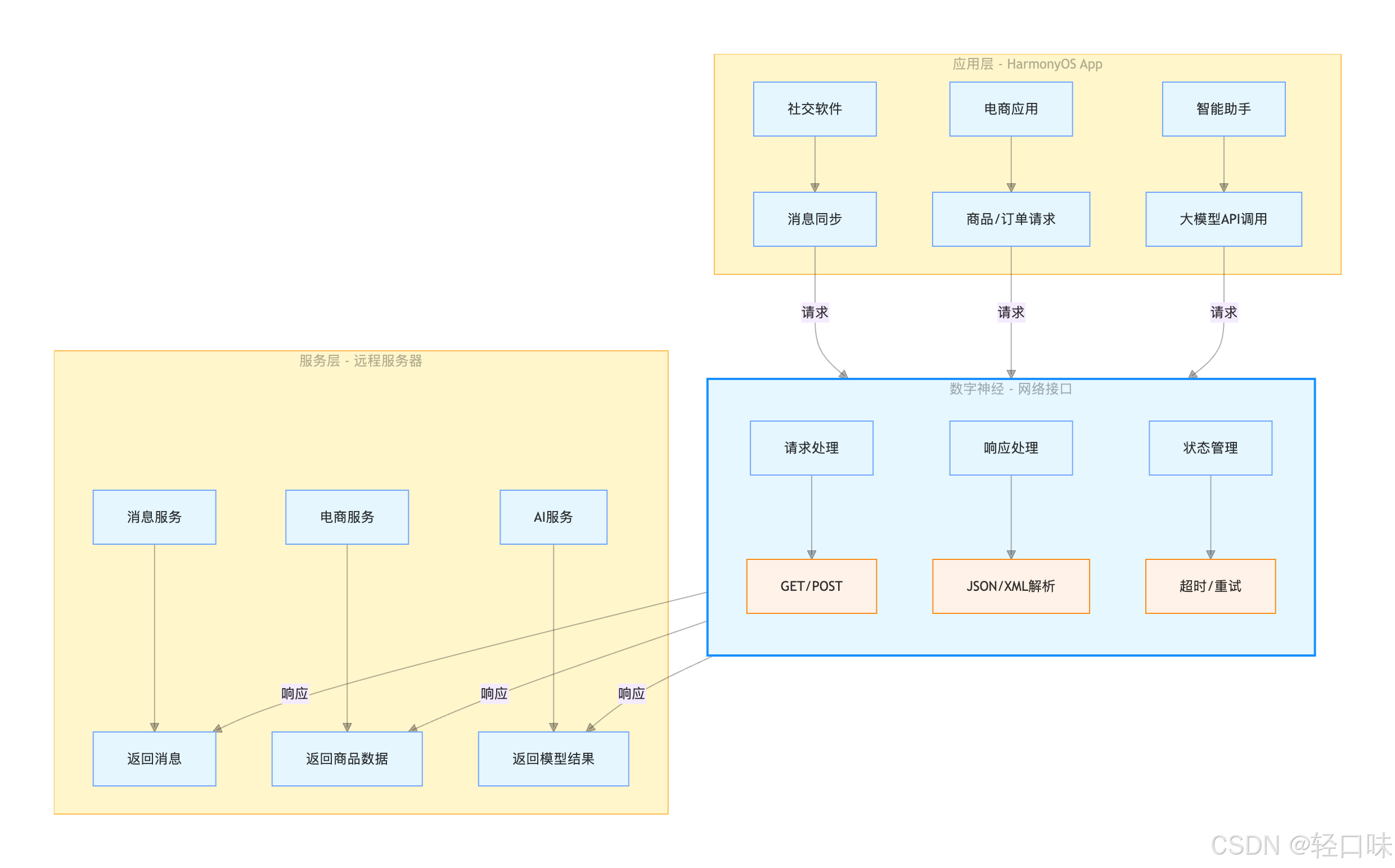
仓颉网络请求API介绍
net.http.*模块介绍
仓颉网络编程提供了Socket、HTTP、WebSocket等通信方式,在net.http.*包下提供,不仅支持客户端请求,还支持创建HTTP服务。以下示例展示了如何使用仓颉进行客户端和服务端编程:
import net.http.*
import std.time.*
import std.sync.*
import std.log.LogLevel
// 1. 构建 Server 实例
let server = ServerBuilder()
.addr("127.0.0.1")
.port(8080)//监听8080端口
.build()
func startServer(): Unit {
// 2. 注册请求处理逻辑
server.distributor.register("/test", {httpContext =>
httpContext.responseBuilder.body("Cangjie Success!")
})
server.logger.level = OFF
// 3. 启动服务
server.serve()
}
func startClient(): Unit {
// 1. 构建 client 实例
let client = ClientBuilder().build()
// 2. 发送 request
let response = client.get("http://127.0.0.1:8080/test")
// 3. 读取response body
let buffer = Array<Byte>(32, item: 0)
let length = response.body.read(buffer)
println(String.fromUtf8(buffer[..length]))
// 4. 关闭连接
client.close()
}
main () {
spawn {
startServer()
}
sleep(Duration.second)
startClient()
}
上面示例搭建了一个简单的http服务,监听本地地址和8080端口,接口路径为test,客户端请求时返回“Cangjie Success!”。
ohos.net.http模块介绍
HarmonyOS 场景下仓颉API提供了ohos.net.http模块发起网络请求,应用可以使用该模块通过HTTP发起一个数据请求,支持常见的GET、POST、OPTIONS、HEAD、PUT、DELETE、TRACE、CONNECT方法。
在该模块下,通过HttpRequest类发起网络请求,支持普通请求和流式请求。通过HttpRequestOptions构造请求方式、请求Header等。接下来介绍使用步骤。
首先申请网络请求权限,导入模块:import ohos.net.http.*
接下来通过public func createHttp(): HttpRequest构造HttpRequest
接着构造HttpRequestOptions,然后通过public func request(url: String, callback: (?BusinessException, ?HttpResponse) -> Unit, options!: ?HttpRequestOptions = None): Unit发起网络请求,在callback中处理服务端响应事件。
最后销毁HttpRequest。
HttpRequestOptions类的构造函数如下:
public class HttpRequestOptions {
public HttpRequestOptions(
public let method!: RequestMethod = RequestMethod.GET,
public let extraData!: ?HttpData = None,
public let expectDataType!: ?HttpDataType = None,
public let usingCache!: Bool = true,
public let priority!: UInt32 = 1,
public let header!: ?HashMap<String, String> = None,
public let readTimeout!: UInt32 = 60000,
public let connectTimeout!: UInt32 = 60000,
public let usingProtocol!: ?HttpProtocol = None,
public let usingProxy!: UsingProxy = USE_DEFAULT,
public let caPath!: ?String = None,
public let resumeFrom!: ?Int64 = None,
public let resumeTo!: ?Int64 = None,
public let clientCert!: ?ClientCert = None,
public let dnsOverHttps!: ?String = None,
public let dnsServers!: ?Array<String> = None,
public let maxLimit!: UInt32 = 5 * 1024 * 1024,
public let multiFormDataList!: ?Array<MultiFormData> = None
) {}
}
包含了请求方式,header,超时时间配置,ca证书路径等,都有默认的值。
下面介绍post请求发送Json数据示例。
var authorization: String = ""
func getHeaderMethod():HashMap<String, String>{
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty<String>(this.authorization)){
LogUtil.d(TAG, "header===: Empty-cookieValue=${authorization}")
return HashMap<String, String>([("content-type", "application/json")])
} else {
//var cookie:String = AppStorage.get<String>("Cookie").getOrThrow()
LogUtil.d(TAG, "header===: Value-cookieValue=${authorization}")
return HashMap<String, String>([("content-type", "application/json"),("authorization",authorization)])
}
}
//post请求
public func httpRequestPost<E>(callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E> {
let option = HttpRequestOptions(
method: RequestMethod.POST, // 可选,默认为http.RequestMethod.GET
usingCache: true, // 可选,默认为true
extraData: HttpData.STRING_DATA("{\"email\":\"${phoneNum}\"}"),
expectDataType: HttpDataType.STRING, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
header:getHeaderMethod(),
readTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
usingProxy: UsingProxy.NOT_USE, //可选,默认不使用网络代理,自API 10开始支持该属性
)
let httpRequest = createHttp();
// 用于订阅HTTP响应头,此接口会比request请求先返回。可以根据业务需要订阅此消息
httpRequest.onHeadersReceive({header: HashMap<String, String> =>
LogUtil.d(TAG, "resp===: header: ${header}")
})
try {
httpRequest.request(http://qignkouwei.com/api/auth/send-code,{ err, resp =>
var responseResult = Option<BaseResponse<E>>.None
if (let Some(e) <- err) {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "exception: ${e.message}")
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(400, e.message, ""))
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
}
if (let Some(r) <- resp) {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "resp===: data:${r.result}")
//数据类解析
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(r.result.toString())
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
} else {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "response is none")
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(404, "response is none", ""))
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
}
callback(responseResult.getOrThrow())
httpRequest.destroy()
},
options: option
)
} catch (exception: Exception) {
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(500, "${exception.message}", "出错了"))
var responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
callback(responseResult)
} finally {
}
}
}
示例中通过header增加了token身份校验。
网络请求封装
上面看起来每次操作都有很多代码,非常繁琐,一般的做法是把网络请求封装成工具,在使用的地方直接调用。
public class HttpService{
let TAG:String = "HttpService"
var authorization: String = ""
//单例
private HttpService() {}
private static var instance: HttpService = HttpService()
public static func getInstance(): HttpService {
return instance
}
public func setAuthorization(token:String){
LogUtil.d(TAG, "setAuthorization:${token}")
this.authorization = "Bearer ${token}";
}
func getHeaderMethod():HashMap<String, String>{
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty<String>(this.authorization)){
LogUtil.d(TAG, "header===: Empty-cookieValue=${authorization}")
return HashMap<String, String>([("content-type", "application/json")])
} else {
//var cookie:String = AppStorage.get<String>("Cookie").getOrThrow()
LogUtil.d(TAG, "header===: Value-cookieValue=${authorization}")
return HashMap<String, String>([("content-type", "application/json"),("authorization",authorization)])
}
}
//get请求
func httpRequestGet<E>(url: String, callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E> {
let option = HttpRequestOptions(
method: RequestMethod.GET, // 可选,默认为http.RequestMethod.GET
expectDataType: HttpDataType.STRING, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
usingCache: true, // 可选,默认为true
priority: 1, // 可选,默认为1
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
header:getHeaderMethod(),
readTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
usingProtocol: HttpProtocol.HTTP1_1, // 可选,协议类型默认值由系统自动指定
usingProxy: UsingProxy.NOT_USE, //可选,默认不使用网络代理,自API 10开始支持该属性
)
return httpRequest(url, option, callback)
}
//post请求
public func httpRequestPost<E>(url: String, params: String, callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E> {
let option = HttpRequestOptions(
method: RequestMethod.POST, // 可选,默认为http.RequestMethod.GET
usingCache: true, // 可选,默认为true
extraData: HttpData.STRING_DATA(params),
expectDataType: HttpDataType.STRING, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
header:getHeaderMethod(),
readTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
usingProxy: UsingProxy.NOT_USE, //可选,默认不使用网络代理,自API 10开始支持该属性
)
return httpRequest(url, option, callback)
}
//put请求
public func httpRequestPut<E>(url: String, params: String, callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E> {
let option = HttpRequestOptions(
method: RequestMethod.PUT, // 可选,默认为http.RequestMethod.GET
usingCache: true, // 可选,默认为true
extraData: HttpData.STRING_DATA(params),
expectDataType: HttpDataType.STRING, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
header:getHeaderMethod(),
readTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
usingProxy: UsingProxy.NOT_USE, //可选,默认不使用网络代理,自API 10开始支持该属性
)
return httpRequest(url, option, callback)
}
public func httpRequestDelete<E>(url: String, params: String, callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E> {
let option = HttpRequestOptions(
method: RequestMethod.DELETE, // 可选,默认为http.RequestMethod.GET
usingCache: true, // 可选,默认为true
extraData: HttpData.STRING_DATA(params),
expectDataType: HttpDataType.STRING, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
header:getHeaderMethod(),
readTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60000ms
usingProxy: UsingProxy.NOT_USE, //可选,默认不使用网络代理,自API 10开始支持该属性
)
return httpRequest(url, option, callback)
}
func httpRequest<E>(url: String, option: HttpRequestOptions, callback: (data:BaseResponse<E>)->Unit) where E <: Serializable<E>{
let httpRequest = createHttp();
// 用于订阅HTTP响应头,此接口会比request请求先返回。可以根据业务需要订阅此消息
httpRequest.onHeadersReceive({header: HashMap<String, String> =>
LogUtil.d(TAG, "resp===: header: ${header}")
})
try {
httpRequest.request(url,{ err, resp =>
var responseResult = Option<BaseResponse<E>>.None
if (let Some(e) <- err) {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "exception: ${e.message}")
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(400, e.message, ""))
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
}
if (let Some(r) <- resp) {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "resp===: data:${r.result}")
//数据类解析
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(r.result.toString())
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
} else {
LogUtil.d(TAG, "response is none")
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(404, "response is none", ""))
responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
}
callback(responseResult.getOrThrow())
httpRequest.destroy()
},
options: option
)
} catch (exception: Exception) {
var jo = JsonUtil.String2JsonObject(NetUtil.getResult(500, "${exception.message}", "出错了"))
var responseResult = JsonUtil.JsonObject2ResponseResult<E>(jo)
callback(responseResult)
} finally {
}
}
}
一般一个APP的和服务端通信,有一些公共的协议字段放在请求header中,比如标识用户身份的token,UA等,这里面封装了获取通用header的方法getHeaderMethod。
接着把不同请求方式的请求封装成GET、POST、DELETE方法,最后在httpRequest发起真正的请求。返回的数据类型是Json,这里做了统一的String到对象的转换。
有了底层请求工具,可以封装不同的请求方法了:
public interface NetApi {
//发送验证码
static func sendLoginCode(params:String, callback:(data:BaseResponse<String>)->Unit){
return HttpService.getInstance().httpRequestPost<String>('http://qingkouwei.com/api/auth/send-code', params, callback)
}
//验证码登录
static func doCodeLogin(params:String, callback:(data:BaseResponse<String>)->Unit){
return HttpService.getInstance().httpRequestPost<String>('http://qingkouwei.com/api/auth/login-code', params, callback)
}
}
使用注意
在实际使用时,HttpRequest请求时启动了子线程,callback回调也在子线程,所以要更新UI需要切换到主线程。
let todosListCallback = {data: BaseResponse<Array<TodoGroupBean>> =>
LogUtil.d(TAG, "getTodosList response")
launch{
if(data.errno == 0){
try{
let todoGroupResponse = data.data.getOrThrow()
}catch (e: NoneValueException) {
PromptAction.showToast(message: "获取列表失败,请稍后重试")
}
}else{
PromptAction.showToast(message: "获取列表失败,请稍后重试")
}
isShowLoading = false
}
}
NetApi.getTodosList(todosListCallback)
在callback中通过launch切换到主线程更新状态变量更新UI。整体使用流程图如下: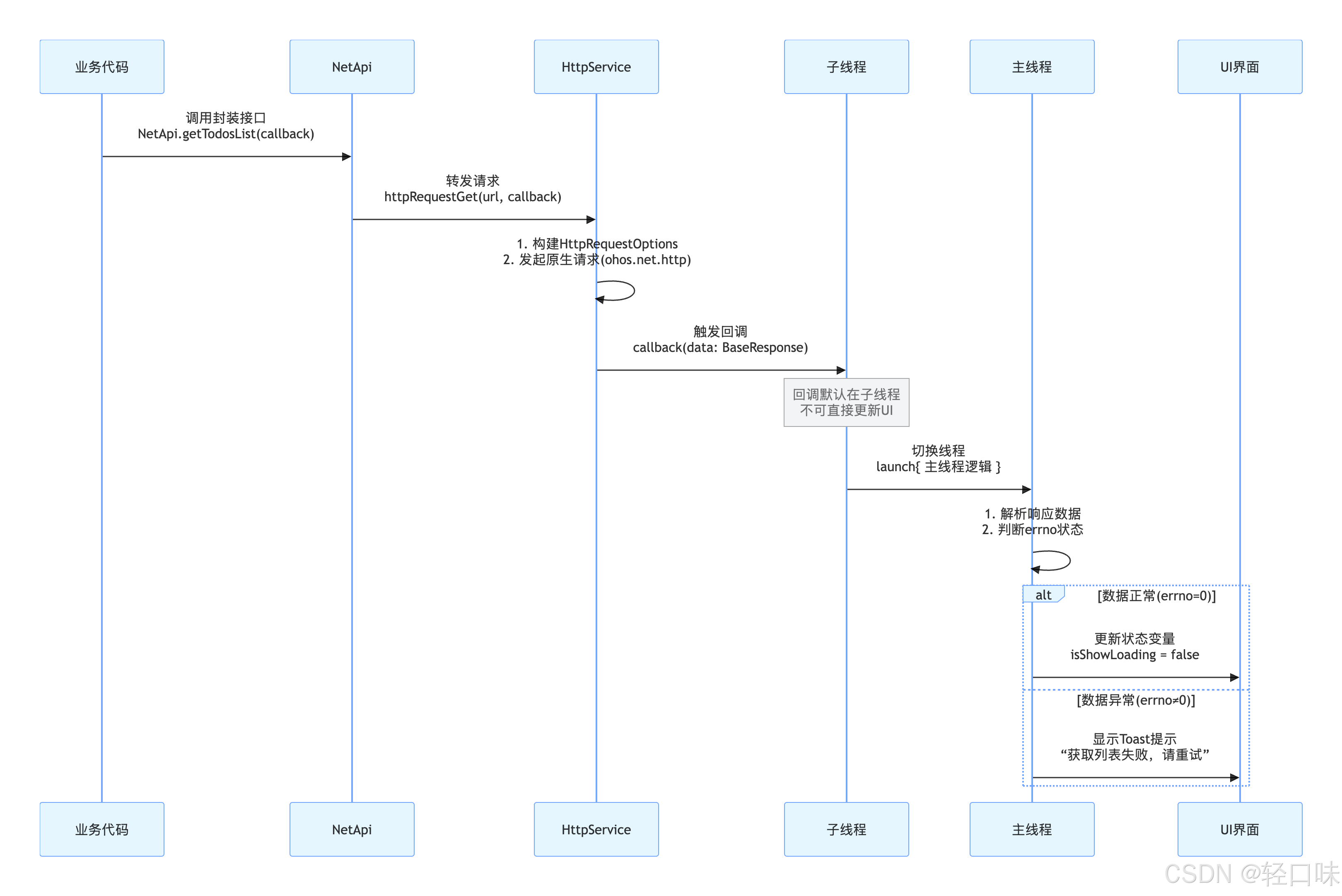
总结
网络接口是应用与外部服务的“数字神经”,决定着稳定性、效率与易用性。在HarmonyOS中,仓颉通过**net.http.***与ohos.net.http提供从Socket/HTTP/WebSocket到HttpRequest的完整能力,支持GET/POST/PUT/DELETE等常用方法、请求头与超时配置、JSON解析及token鉴权;同时可通过onHeadersReceive订阅响应头、在回调中切换主线程更新UI。为降低样板代码,文中封装了HttpService与NetApi,统一header、timeout、JSON转换与错误处理,使接口调用更简洁、可维护性更高。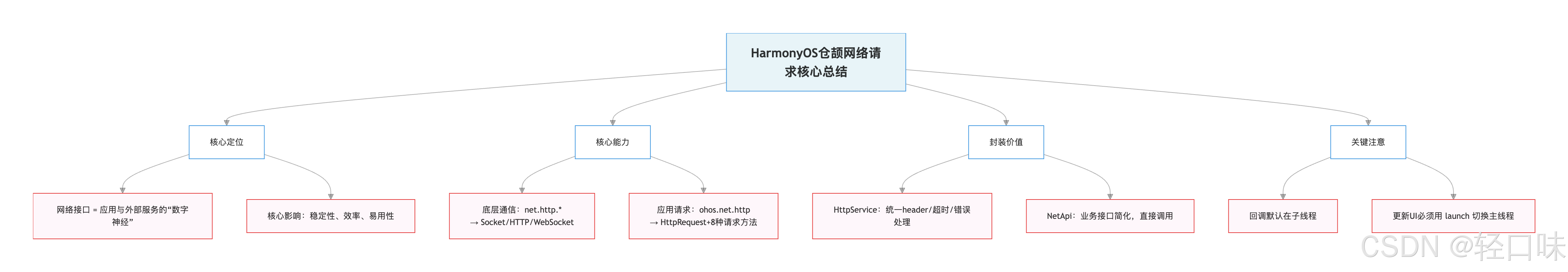
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献51条内容
已为社区贡献51条内容









所有评论(0)