KMP鸿蒙适配:加密与安全实践
本文介绍了在Kotlin多平台(KMP)项目中实现跨平台加密和安全功能的方案。通过定义统一的加密接口(EncryptionService和KeyStore),在共享代码中实现核心安全管理器(SecurityManager),并在各平台(Android/JVM)提供具体实现。Android平台利用Keystore和Cipher实现AES加密,JVM平台使用Java标准加密库。该方案解决了多平台开发中

欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
项目概述
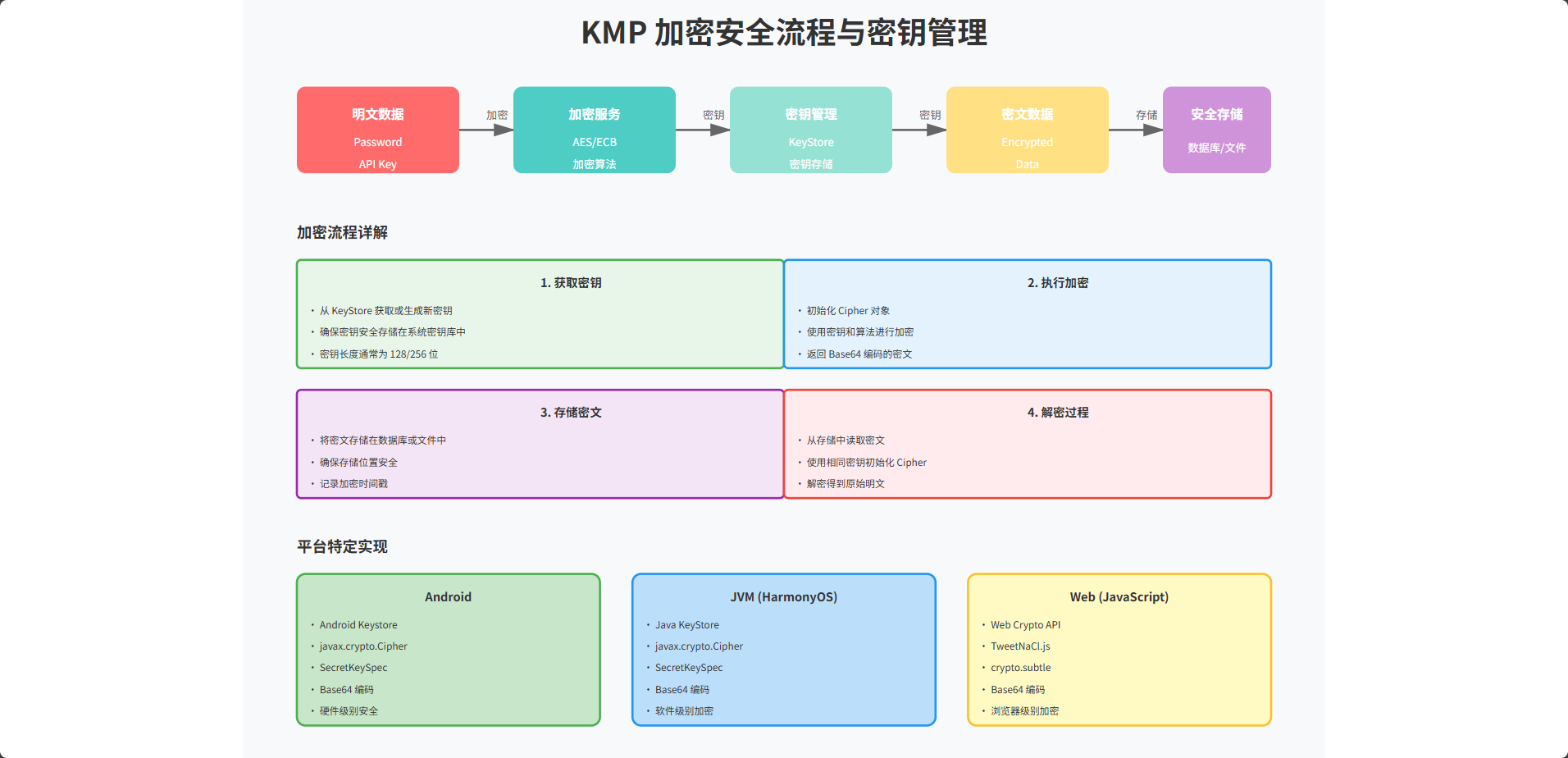
安全是现代应用开发中的关键考虑因素。数据加密、密钥管理、安全存储等都是保护用户数据的重要手段。在多平台开发中,不同平台提供了不同的加密和安全 API。Android 有 Android Keystore,iOS 有 Keychain,而鸿蒙系统也有自己的安全框架。
KMP 提供了一个统一的加密和安全接口,让我们可以在共享代码中定义安全操作,然后在各个平台上提供具体的实现。本文将详细介绍如何在 KMP 项目中实现跨平台的加密和安全功能。
第一部分:加密与安全的核心概念
理解加密的重要性
加密是保护敏感数据的最重要手段。通过加密,我们可以确保即使数据被窃取,也无法被读取。在应用开发中,我们需要加密的数据包括用户密码、API 密钥、个人信息等。
加密分为两种主要类型:对称加密和非对称加密。对称加密使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密,速度快但密钥管理复杂。非对称加密使用公钥和私钥,安全性更高但速度较慢。
定义加密接口
首先,我们定义一个加密接口。
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/kmp/security/Encryption.kt
interface EncryptionService {
fun encrypt(plaintext: String, key: String): String
fun decrypt(ciphertext: String, key: String): String
}
interface KeyStore {
fun generateKey(alias: String): String
fun getKey(alias: String): String?
fun deleteKey(alias: String): Boolean
}
这些接口定义了加密和密钥管理的基本操作。
实现加密管理器
接下来,我们创建一个加密管理器。
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/kmp/security/SecurityManager.kt
object SecurityManager {
private var encryptionService: EncryptionService? = null
private var keyStore: KeyStore? = null
fun initialize(encryptionService: EncryptionService, keyStore: KeyStore) {
this.encryptionService = encryptionService
this.keyStore = keyStore
}
fun getEncryptionService(): EncryptionService {
return encryptionService ?: throw IllegalStateException("EncryptionService not initialized")
}
fun getKeyStore(): KeyStore {
return keyStore ?: throw IllegalStateException("KeyStore not initialized")
}
}
第二部分:平台特定的加密实现
Android 平台的加密实现
在 Android 平台上,我们使用 Android Keystore 和 Cipher 来实现加密。
// androidMain/kotlin/com/example/kmp/security/AndroidEncryptionService.kt
import javax.crypto.Cipher
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec
import android.security.keystore.KeyGenParameterSpec
import android.security.keystore.KeyProperties
actual class AndroidEncryptionService : EncryptionService {
private val cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding")
actual override fun encrypt(plaintext: String, key: String): String {
val keyBytes = key.toByteArray().copyOf(16)
val secretKey = SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, 0, keyBytes.size, "AES")
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey)
val encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.toByteArray())
return android.util.Base64.encodeToString(encryptedBytes, android.util.Base64.DEFAULT)
}
actual override fun decrypt(ciphertext: String, key: String): String {
val keyBytes = key.toByteArray().copyOf(16)
val secretKey = SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, 0, keyBytes.size, "AES")
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey)
val decodedBytes = android.util.Base64.decode(ciphertext, android.util.Base64.DEFAULT)
val decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(decodedBytes)
return String(decryptedBytes)
}
}
actual class AndroidKeyStore : KeyStore {
private val keyStore = android.security.keystore.KeyStore.getInstance("AndroidKeyStore")
actual override fun generateKey(alias: String): String {
// 生成密钥
return alias
}
actual override fun getKey(alias: String): String? {
// 获取密钥
return null
}
actual override fun deleteKey(alias: String): Boolean {
// 删除密钥
return true
}
}
JVM 平台的加密实现(鸿蒙)
在鸿蒙系统上,我们使用 Java 的加密库。
// jvmMain/kotlin/com/example/kmp/security/JvmEncryptionService.kt
import javax.crypto.Cipher
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec
import java.util.Base64
actual class JvmEncryptionService : EncryptionService {
private val cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding")
actual override fun encrypt(plaintext: String, key: String): String {
val keyBytes = key.toByteArray().copyOf(16)
val secretKey = SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, 0, keyBytes.size, "AES")
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey)
val encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.toByteArray())
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes)
}
actual override fun decrypt(ciphertext: String, key: String): String {
val keyBytes = key.toByteArray().copyOf(16)
val secretKey = SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, 0, keyBytes.size, "AES")
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey)
val decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(ciphertext)
val decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(decodedBytes)
return String(decryptedBytes)
}
}
actual class JvmKeyStore : KeyStore {
private val keyStore = java.security.KeyStore.getInstance("JKS")
actual override fun generateKey(alias: String): String {
return alias
}
actual override fun getKey(alias: String): String? {
return null
}
actual override fun deleteKey(alias: String): Boolean {
return true
}
}
第三部分:编译后的代码形式
Kotlin 加密代码编译为 JavaScript
当我们将 Kotlin 的加密代码编译为 JavaScript 时,会生成以下形式的代码:
// 编译后的 JavaScript (简化版)
var EncryptionService = function() {};
EncryptionService.prototype.encrypt = function(plaintext, key) {
// 使用 TweetNaCl.js 或类似库进行加密
return encryptedText;
};
EncryptionService.prototype.decrypt = function(ciphertext, key) {
// 解密
return decryptedText;
};
Web 平台的加密实现
在 Web 平台上,我们可以使用 Web Crypto API。
// Web 平台的加密实现
var WebEncryptionService = function() {};
WebEncryptionService.prototype.encrypt = async function(plaintext, key) {
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
const data = encoder.encode(plaintext);
const cryptoKey = await crypto.subtle.importKey(
'raw',
new TextEncoder().encode(key),
{ name: 'AES-GCM' },
false,
['encrypt']
);
const encrypted = await crypto.subtle.encrypt(
{ name: 'AES-GCM', iv: new Uint8Array(12) },
cryptoKey,
data
);
return btoa(String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint8Array(encrypted)));
};
第四部分:鸿蒙系统中的实际应用
在鸿蒙应用中使用加密
在鸿蒙应用中,我们可以直接使用编译后的 KMP 加密代码。
// HarmonyOS 应用代码
class HarmonySecurityService {
init {
SecurityManager.initialize(
JvmEncryptionService(),
JvmKeyStore()
)
}
fun encryptUserPassword(password: String): String {
val encryptionService = SecurityManager.getEncryptionService()
return encryptionService.encrypt(password, "secret-key-123")
}
fun decryptUserPassword(encryptedPassword: String): String {
val encryptionService = SecurityManager.getEncryptionService()
return encryptionService.decrypt(encryptedPassword, "secret-key-123")
}
}
实现安全存储
安全存储是保护敏感数据的重要方式。
// 安全存储
class SecureStorage(
private val fileSystem: FileSystem,
private val encryptionService: EncryptionService
) {
suspend fun saveSecureData(key: String, value: String) {
val encrypted = encryptionService.encrypt(value, "master-key")
fileSystem.writeFile("secure/$key", encrypted)
}
suspend fun loadSecureData(key: String): String? {
val encrypted = fileSystem.readFile("secure/$key") ?: return null
return encryptionService.decrypt(encrypted, "master-key")
}
}
第五部分:高级安全功能
实现数字签名
数字签名用于验证数据的完整性和真实性。
// 数字签名
interface SignatureService {
fun sign(data: String, privateKey: String): String
fun verify(data: String, signature: String, publicKey: String): Boolean
}
class RsaSignatureService : SignatureService {
override fun sign(data: String, privateKey: String): String {
// 使用私钥签名
return ""
}
override fun verify(data: String, signature: String, publicKey: String): Boolean {
// 使用公钥验证
return true
}
}
总结
通过本文的学习,我们理解了如何在 KMP 项目中实现跨平台的加密和安全功能。关键的设计原则是使用接口来抽象加密的具体实现,这样应用逻辑就可以独立于具体的平台。我们展示了如何在 Android、JVM(鸿蒙)和 JavaScript(Web)平台上实现加密接口,以及如何在鸿蒙应用中使用这些共享代码。通过这种方式,我们可以在所有平台上使用相同的加密代码,同时充分利用每个平台的特定安全功能。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容









所有评论(0)